Cardiac Arrest Blood Pressure - When the heart's mechanical function stops, there is no blood flow through the body, known as cardiac arrest. Blood pressure is one modifiable physiological target in patients treated in the intensive care unit after cardiac arrest. Target a mean arterial pressure (1/3 systolic bp + 2/3 diastolic bp) greater than 65 mmhg, or systolic blood pressure greater than 90 mmhg. The american heart association explains the causes of cardiac arrest, the warning sign of cardiac arrest, the symptoms of cardiac arrest,.
When the heart's mechanical function stops, there is no blood flow through the body, known as cardiac arrest. Blood pressure is one modifiable physiological target in patients treated in the intensive care unit after cardiac arrest. The american heart association explains the causes of cardiac arrest, the warning sign of cardiac arrest, the symptoms of cardiac arrest,. Target a mean arterial pressure (1/3 systolic bp + 2/3 diastolic bp) greater than 65 mmhg, or systolic blood pressure greater than 90 mmhg.
When the heart's mechanical function stops, there is no blood flow through the body, known as cardiac arrest. The american heart association explains the causes of cardiac arrest, the warning sign of cardiac arrest, the symptoms of cardiac arrest,. Blood pressure is one modifiable physiological target in patients treated in the intensive care unit after cardiac arrest. Target a mean arterial pressure (1/3 systolic bp + 2/3 diastolic bp) greater than 65 mmhg, or systolic blood pressure greater than 90 mmhg.
(PDF) Optimal oxygen and mean arterial blood pressure targets after
Blood pressure is one modifiable physiological target in patients treated in the intensive care unit after cardiac arrest. When the heart's mechanical function stops, there is no blood flow through the body, known as cardiac arrest. Target a mean arterial pressure (1/3 systolic bp + 2/3 diastolic bp) greater than 65 mmhg, or systolic blood pressure greater than 90 mmhg..
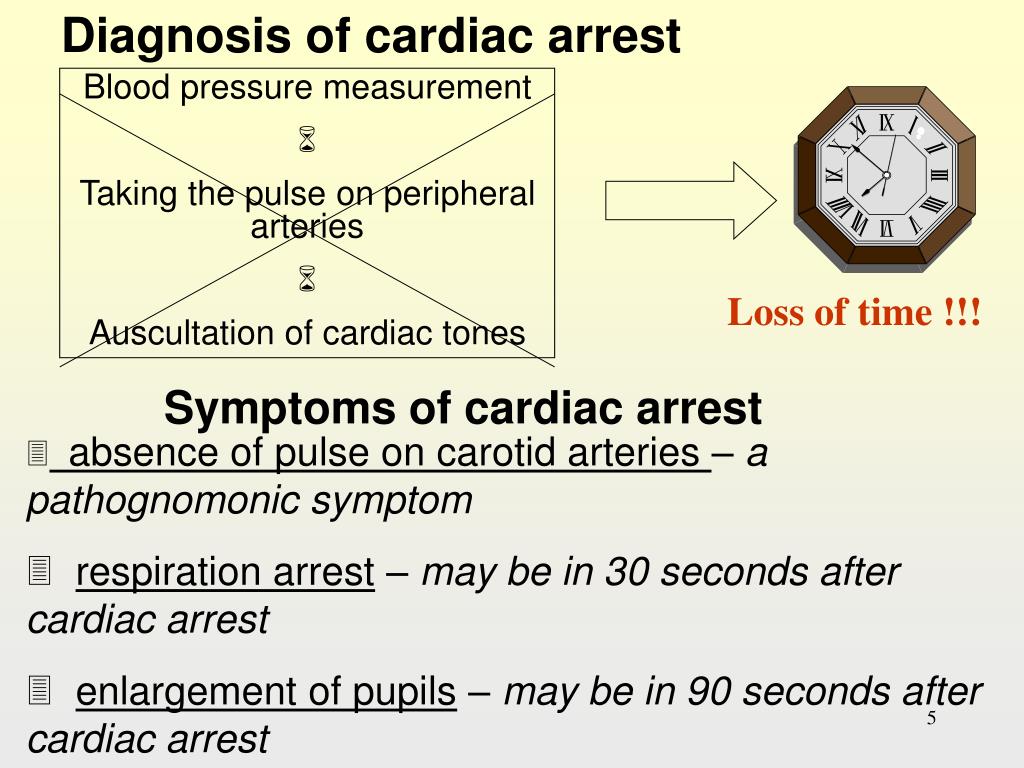
PPT CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION PowerPoint Presentation ID48299
Target a mean arterial pressure (1/3 systolic bp + 2/3 diastolic bp) greater than 65 mmhg, or systolic blood pressure greater than 90 mmhg. When the heart's mechanical function stops, there is no blood flow through the body, known as cardiac arrest. The american heart association explains the causes of cardiac arrest, the warning sign of cardiac arrest, the symptoms.
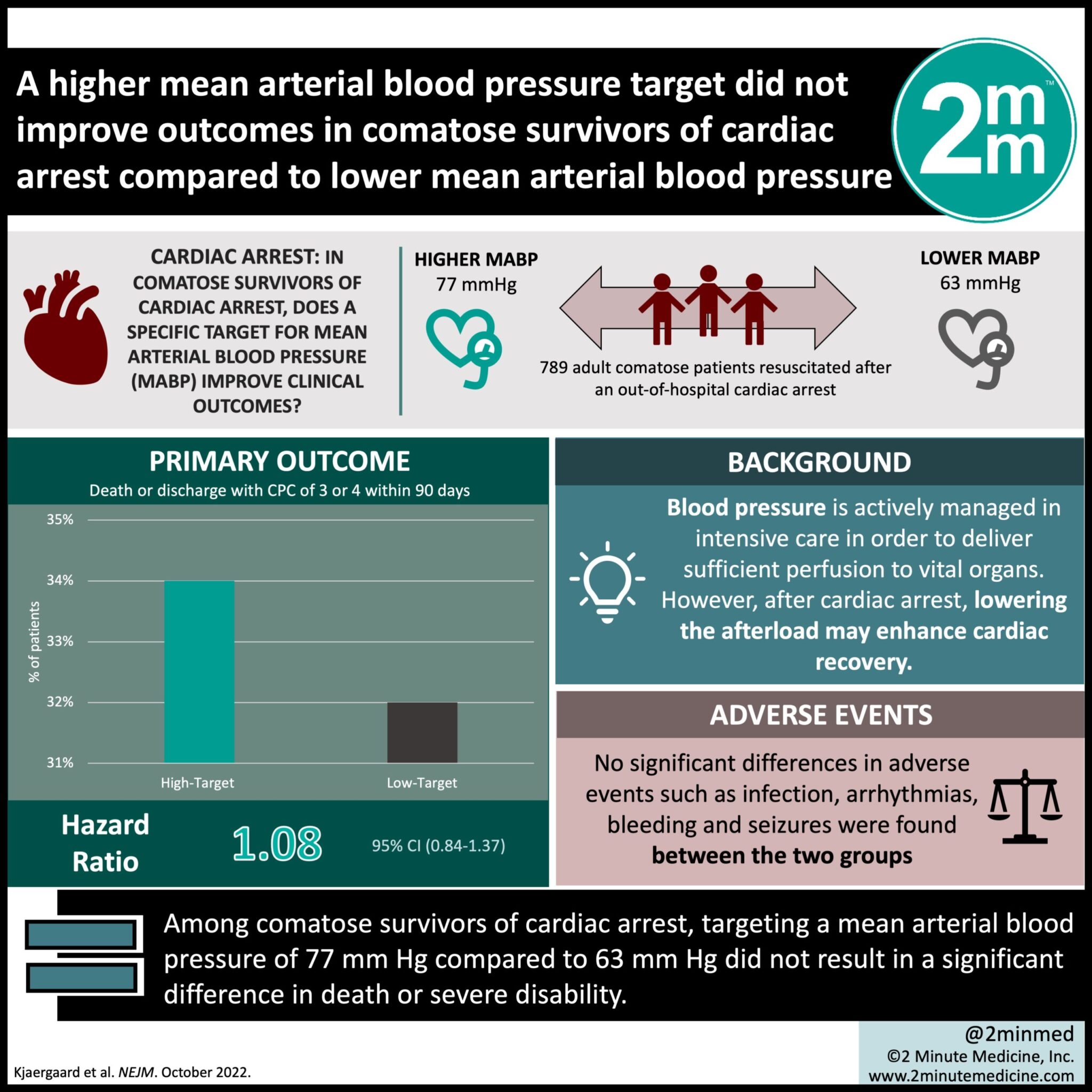
VisualAbstract Higher mean arterial blood pressure targets did not
Target a mean arterial pressure (1/3 systolic bp + 2/3 diastolic bp) greater than 65 mmhg, or systolic blood pressure greater than 90 mmhg. When the heart's mechanical function stops, there is no blood flow through the body, known as cardiac arrest. Blood pressure is one modifiable physiological target in patients treated in the intensive care unit after cardiac arrest..
BloodPressure Targets in Comatose Survivors of Cardiac Arrest NEJM
Blood pressure is one modifiable physiological target in patients treated in the intensive care unit after cardiac arrest. When the heart's mechanical function stops, there is no blood flow through the body, known as cardiac arrest. Target a mean arterial pressure (1/3 systolic bp + 2/3 diastolic bp) greater than 65 mmhg, or systolic blood pressure greater than 90 mmhg..
BloodPressure Targets in Comatose Survivors of Cardiac Arrest New
The american heart association explains the causes of cardiac arrest, the warning sign of cardiac arrest, the symptoms of cardiac arrest,. Target a mean arterial pressure (1/3 systolic bp + 2/3 diastolic bp) greater than 65 mmhg, or systolic blood pressure greater than 90 mmhg. Blood pressure is one modifiable physiological target in patients treated in the intensive care unit.
A Minute by Minute Guide to What Happens During CPR ProTrainings
Target a mean arterial pressure (1/3 systolic bp + 2/3 diastolic bp) greater than 65 mmhg, or systolic blood pressure greater than 90 mmhg. Blood pressure is one modifiable physiological target in patients treated in the intensive care unit after cardiac arrest. The american heart association explains the causes of cardiac arrest, the warning sign of cardiac arrest, the symptoms.
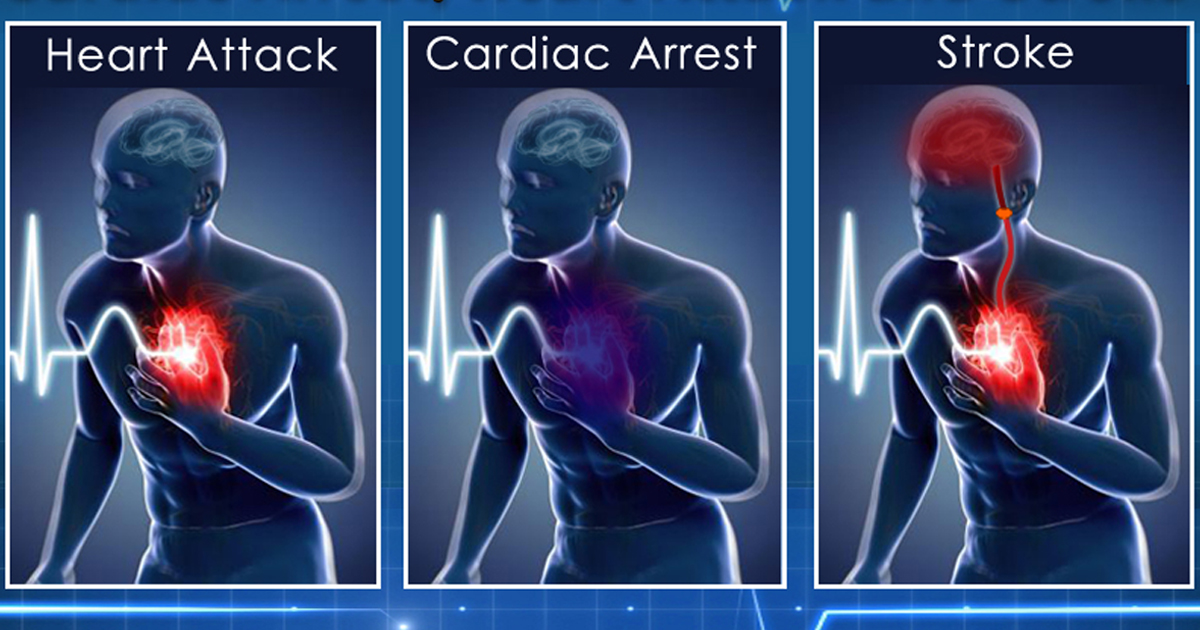
Learn the Key Differences Among, Cardiac Arrest, Heart Attack and
Blood pressure is one modifiable physiological target in patients treated in the intensive care unit after cardiac arrest. When the heart's mechanical function stops, there is no blood flow through the body, known as cardiac arrest. Target a mean arterial pressure (1/3 systolic bp + 2/3 diastolic bp) greater than 65 mmhg, or systolic blood pressure greater than 90 mmhg..
How to identify a Cardiac Arrest Save a Life for Scotland
Blood pressure is one modifiable physiological target in patients treated in the intensive care unit after cardiac arrest. When the heart's mechanical function stops, there is no blood flow through the body, known as cardiac arrest. Target a mean arterial pressure (1/3 systolic bp + 2/3 diastolic bp) greater than 65 mmhg, or systolic blood pressure greater than 90 mmhg..
Blood pressure targets and management during postcardiac arrest care
When the heart's mechanical function stops, there is no blood flow through the body, known as cardiac arrest. The american heart association explains the causes of cardiac arrest, the warning sign of cardiac arrest, the symptoms of cardiac arrest,. Blood pressure is one modifiable physiological target in patients treated in the intensive care unit after cardiac arrest. Target a mean.
Optimum Blood Pressure in Patients With Shock After Acute Myocardial
When the heart's mechanical function stops, there is no blood flow through the body, known as cardiac arrest. Blood pressure is one modifiable physiological target in patients treated in the intensive care unit after cardiac arrest. The american heart association explains the causes of cardiac arrest, the warning sign of cardiac arrest, the symptoms of cardiac arrest,. Target a mean.
The American Heart Association Explains The Causes Of Cardiac Arrest, The Warning Sign Of Cardiac Arrest, The Symptoms Of Cardiac Arrest,.
When the heart's mechanical function stops, there is no blood flow through the body, known as cardiac arrest. Blood pressure is one modifiable physiological target in patients treated in the intensive care unit after cardiac arrest. Target a mean arterial pressure (1/3 systolic bp + 2/3 diastolic bp) greater than 65 mmhg, or systolic blood pressure greater than 90 mmhg.