Cardiac Arrest Brain Injury - Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of.
Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest.
In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive.
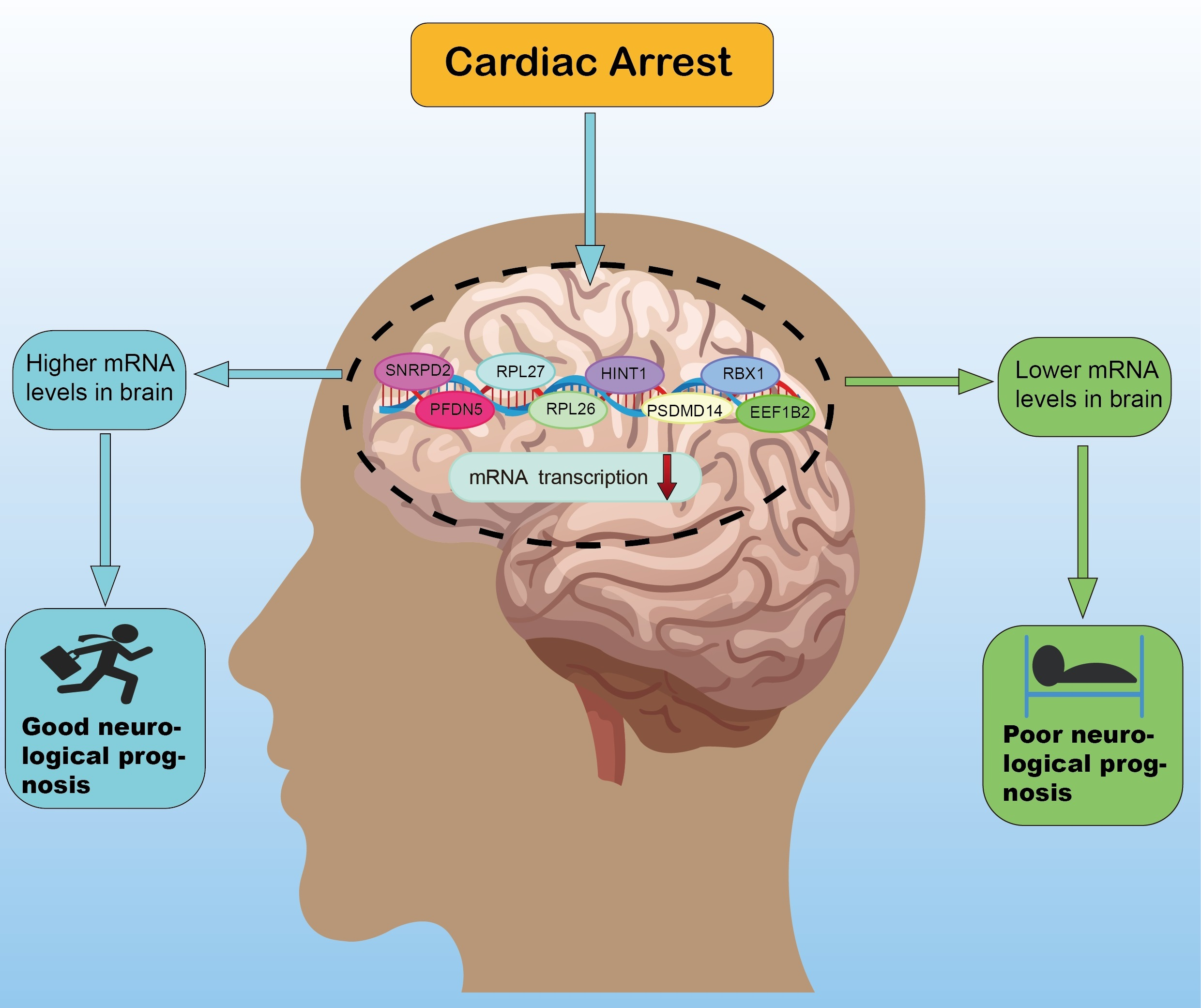
Identification and Validation of Novel Potential Pathogenesis and
Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest. In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of.
Improving After PostCardiac Arrest Brain Injury A Scientific
In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest.
Frontiers Long Term Cognitive Function After Cardiac Arrest A Mini
In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of.
Improving After PostCardiac Arrest Brain Injury A Scientific
In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest.
Brain injury after cardiac arrest The Lancet
In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest.
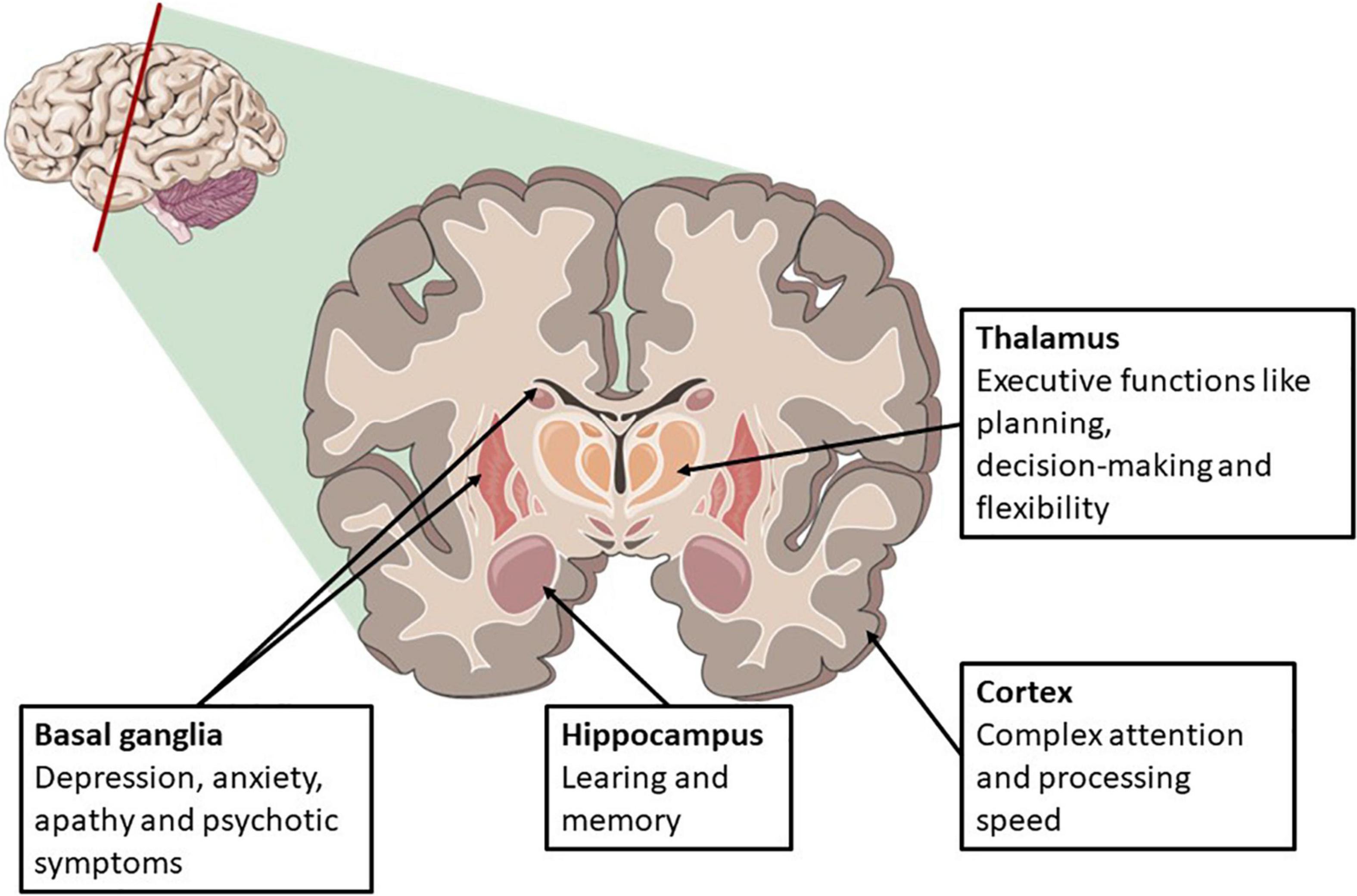
Regional distribution of anoxic brain injury after cardiac arrest
Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest.
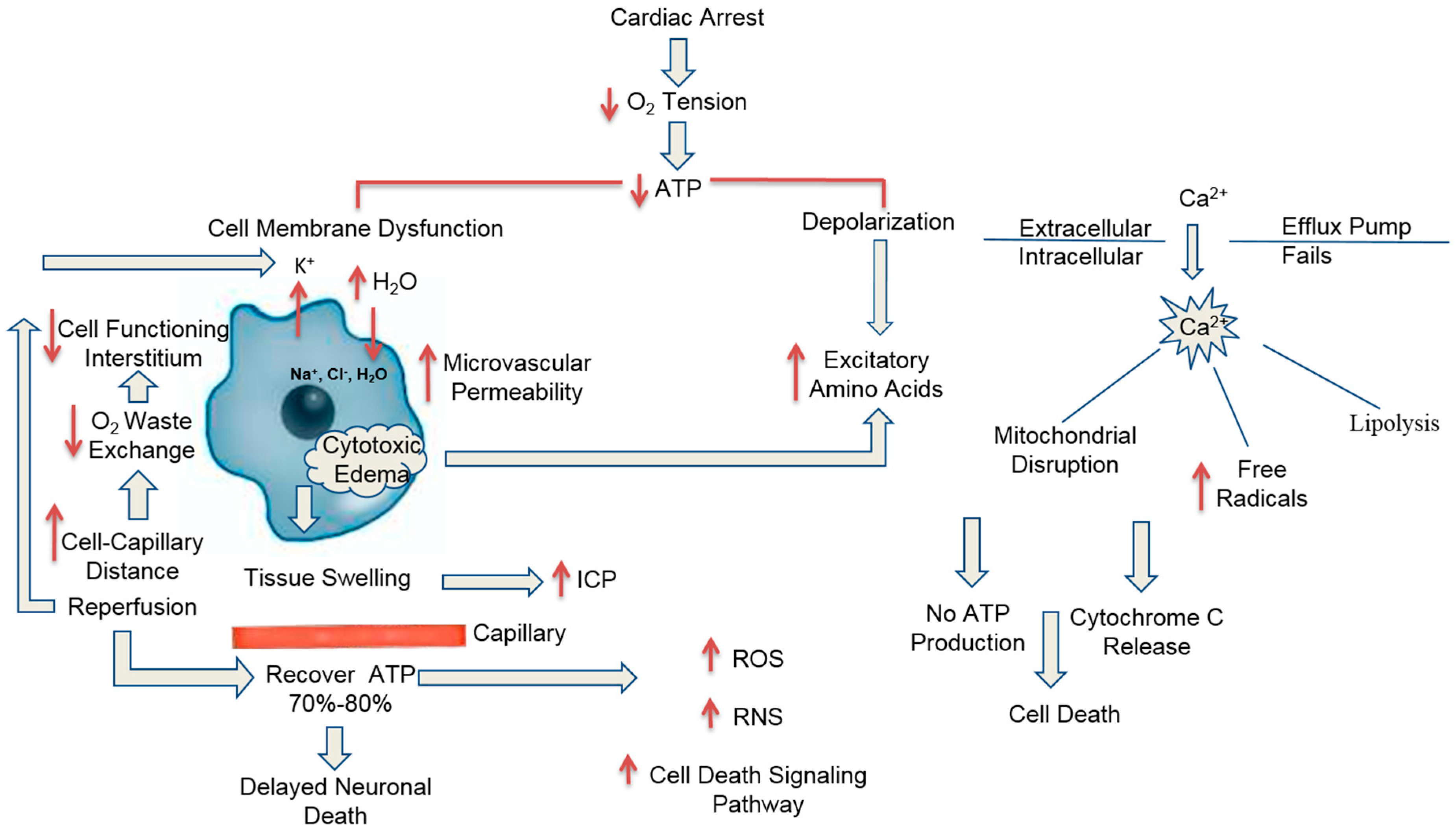
Pathophysiology and the Monitoring Methods for Cardiac Arrest
Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive.
The Lancet on Twitter "Brain injury after cardiac arrest remains a
Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest.
Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation for Out‐of‐Hospital
Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which.
Improving After PostCardiac Arrest Brain Injury A Scientific
Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest. In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which. Most people who experience cardiac arrest do not survive.
Most People Who Experience Cardiac Arrest Do Not Survive.
Explore the mechanisms, consequences, and treatment strategies for brain injury following cardiac arrest. Among those who do, there is risk of neurologic dysfunction, brain injury, disorders of. In simple terms, cardiac arrest means no effective contraction of the heart muscle and no blood flow to the brain, which.