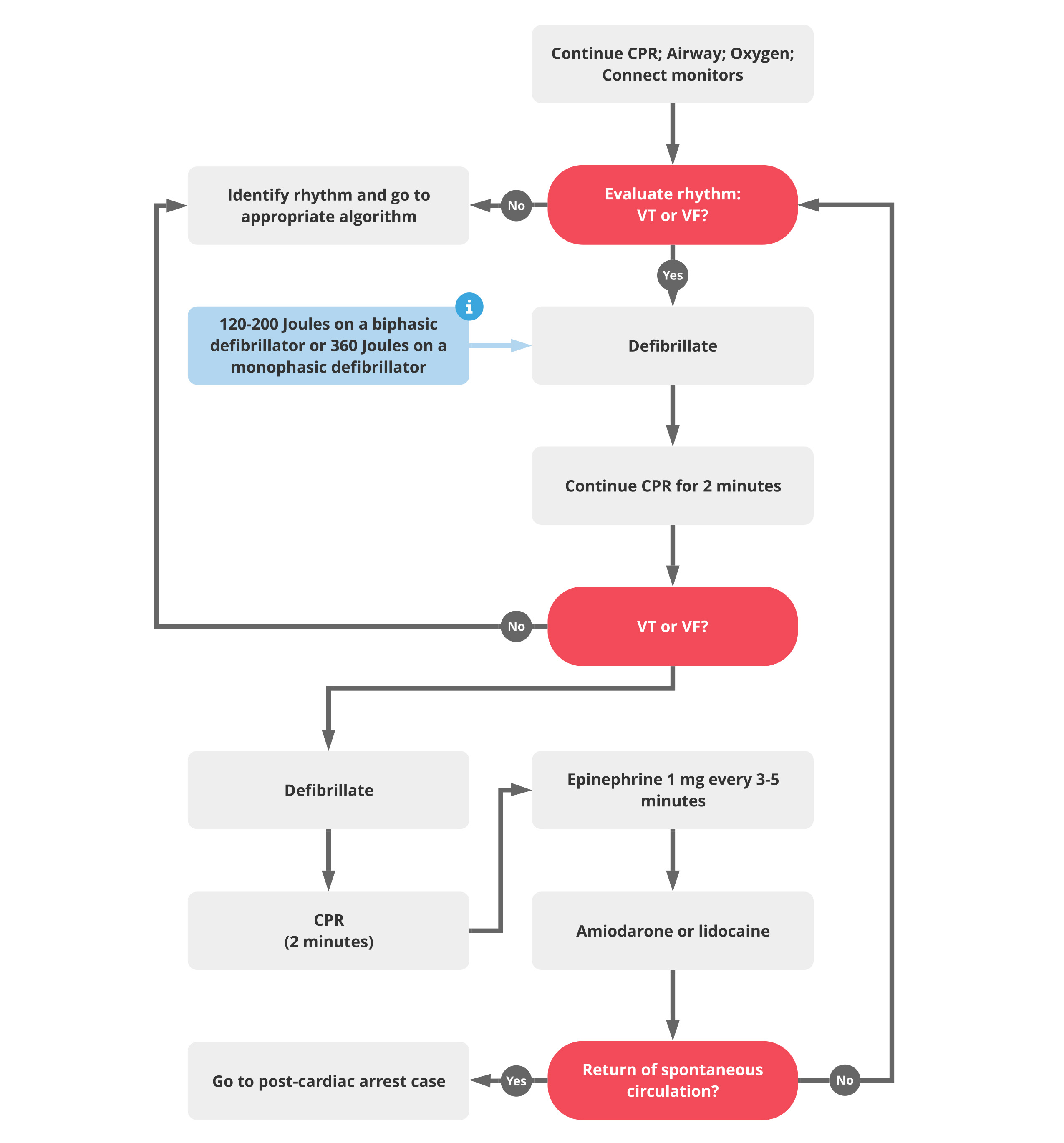
Cardiac Arrest Code - The codes i46.2, i46.8, and i46.9 provide specific classifications that help in identifying the cause of cardiac arrest, which can significantly impact. Adult cardiac arrest circular algorithm. The sudden cessation of cardiac activity so that the victim subject/patient becomes unresponsive, without normal breathing and no signs of. Browse the codes by section, type, exclusions, and.
Browse the codes by section, type, exclusions, and. The codes i46.2, i46.8, and i46.9 provide specific classifications that help in identifying the cause of cardiac arrest, which can significantly impact. The sudden cessation of cardiac activity so that the victim subject/patient becomes unresponsive, without normal breathing and no signs of. Adult cardiac arrest circular algorithm.
Adult cardiac arrest circular algorithm. The codes i46.2, i46.8, and i46.9 provide specific classifications that help in identifying the cause of cardiac arrest, which can significantly impact. Browse the codes by section, type, exclusions, and. The sudden cessation of cardiac activity so that the victim subject/patient becomes unresponsive, without normal breathing and no signs of.
Tandem Codes A Novel Cardiac Arrest Care Model in COVID19
Browse the codes by section, type, exclusions, and. Adult cardiac arrest circular algorithm. The sudden cessation of cardiac activity so that the victim subject/patient becomes unresponsive, without normal breathing and no signs of. The codes i46.2, i46.8, and i46.9 provide specific classifications that help in identifying the cause of cardiac arrest, which can significantly impact.
Intraoperative Crisis Checklist / Code Red / Cardiac Arrest Download
The sudden cessation of cardiac activity so that the victim subject/patient becomes unresponsive, without normal breathing and no signs of. The codes i46.2, i46.8, and i46.9 provide specific classifications that help in identifying the cause of cardiac arrest, which can significantly impact. Adult cardiac arrest circular algorithm. Browse the codes by section, type, exclusions, and.
Day 2 Rev ppt download
Browse the codes by section, type, exclusions, and. Adult cardiac arrest circular algorithm. The codes i46.2, i46.8, and i46.9 provide specific classifications that help in identifying the cause of cardiac arrest, which can significantly impact. The sudden cessation of cardiac activity so that the victim subject/patient becomes unresponsive, without normal breathing and no signs of.
VTach ACLS Training Advanced Cardiac Life Support
The sudden cessation of cardiac activity so that the victim subject/patient becomes unresponsive, without normal breathing and no signs of. Browse the codes by section, type, exclusions, and. The codes i46.2, i46.8, and i46.9 provide specific classifications that help in identifying the cause of cardiac arrest, which can significantly impact. Adult cardiac arrest circular algorithm.
AHA ACLS Megacode Scenarios Copy Cardiac Arrest Cardiopulmonary
Adult cardiac arrest circular algorithm. Browse the codes by section, type, exclusions, and. The codes i46.2, i46.8, and i46.9 provide specific classifications that help in identifying the cause of cardiac arrest, which can significantly impact. The sudden cessation of cardiac activity so that the victim subject/patient becomes unresponsive, without normal breathing and no signs of.
Printable Acls Algorithms Ekg
Adult cardiac arrest circular algorithm. The codes i46.2, i46.8, and i46.9 provide specific classifications that help in identifying the cause of cardiac arrest, which can significantly impact. Browse the codes by section, type, exclusions, and. The sudden cessation of cardiac activity so that the victim subject/patient becomes unresponsive, without normal breathing and no signs of.
Cardiac Arrest
Adult cardiac arrest circular algorithm. Browse the codes by section, type, exclusions, and. The sudden cessation of cardiac activity so that the victim subject/patient becomes unresponsive, without normal breathing and no signs of. The codes i46.2, i46.8, and i46.9 provide specific classifications that help in identifying the cause of cardiac arrest, which can significantly impact.
PPT Hospital Emergency Codes and Procedures PowerPoint Presentation
The sudden cessation of cardiac activity so that the victim subject/patient becomes unresponsive, without normal breathing and no signs of. The codes i46.2, i46.8, and i46.9 provide specific classifications that help in identifying the cause of cardiac arrest, which can significantly impact. Browse the codes by section, type, exclusions, and. Adult cardiac arrest circular algorithm.
Cardiac Arrest Code Blue Program Overview Access TeleCare
Adult cardiac arrest circular algorithm. The sudden cessation of cardiac activity so that the victim subject/patient becomes unresponsive, without normal breathing and no signs of. Browse the codes by section, type, exclusions, and. The codes i46.2, i46.8, and i46.9 provide specific classifications that help in identifying the cause of cardiac arrest, which can significantly impact.
Leading a Cardiac Arrest — Critical Care Time
The sudden cessation of cardiac activity so that the victim subject/patient becomes unresponsive, without normal breathing and no signs of. Adult cardiac arrest circular algorithm. The codes i46.2, i46.8, and i46.9 provide specific classifications that help in identifying the cause of cardiac arrest, which can significantly impact. Browse the codes by section, type, exclusions, and.
The Codes I46.2, I46.8, And I46.9 Provide Specific Classifications That Help In Identifying The Cause Of Cardiac Arrest, Which Can Significantly Impact.
The sudden cessation of cardiac activity so that the victim subject/patient becomes unresponsive, without normal breathing and no signs of. Adult cardiac arrest circular algorithm. Browse the codes by section, type, exclusions, and.