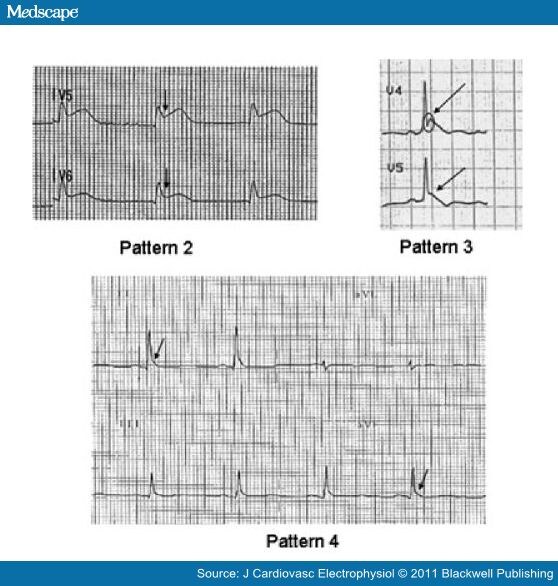
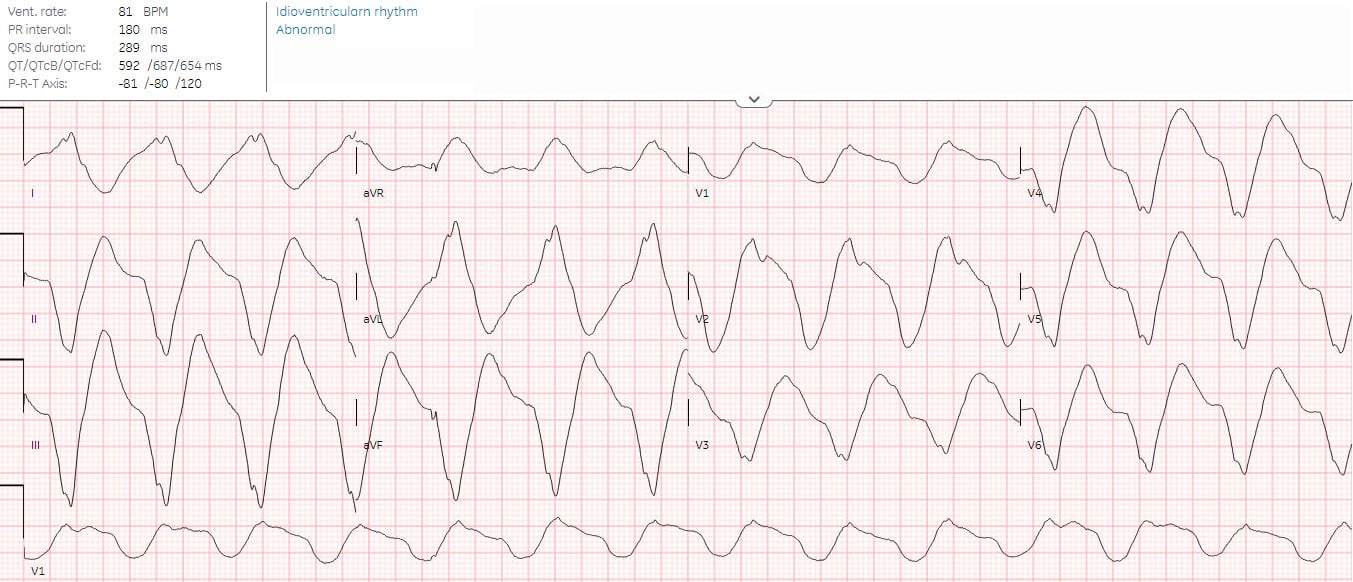
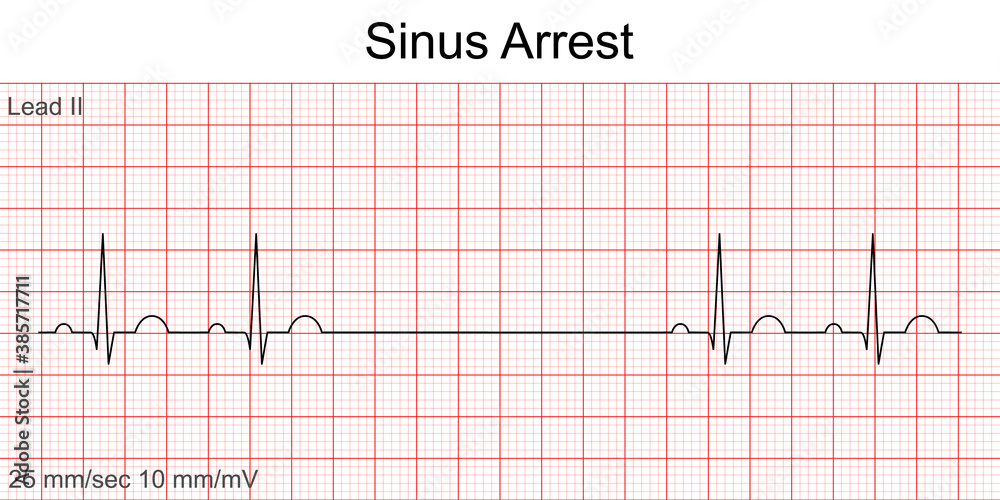
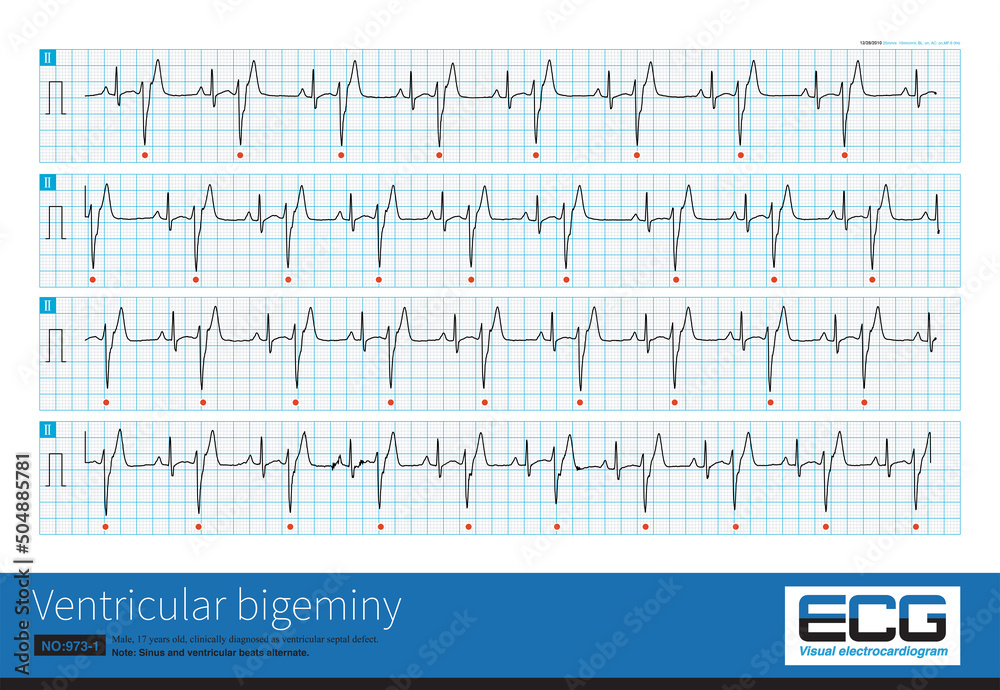
Cardiac Arrest On Ecg - Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. There are four primary alterations in the. Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial to the. The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002).
Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. There are four primary alterations in the. The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial to the. Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest:
Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. There are four primary alterations in the. During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial to the.
Sudden Cardiac Arrest ECG Repolarization After Resuscitation
There are four primary alterations in the. During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial to the. Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of.
ECG Interpretation in Cardiac Arrest ECG Cases Emergency Medicine Cases
There are four primary alterations in the. Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial to the. The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and.
Vetor de Electrocardiogram show Sinus arrest pattern. Cardiac
Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. There are four primary alterations in the. Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial.
ECG Interpretation in Cardiac Arrest ECG Cases Emergency Medicine Cases
The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. There are four primary alterations in the. During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial.
Part 12 Cardiac Arrest in Special Situations Circulation
Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). There are four primary alterations in the. Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial.
arrhythmia, background, cardiac, cardiac arrest, cardiogram, cardiology
There are four primary alterations in the. Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial.
Case A8. Extensive Anterolateral Infarction leading to cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial to the. There are four primary alterations.
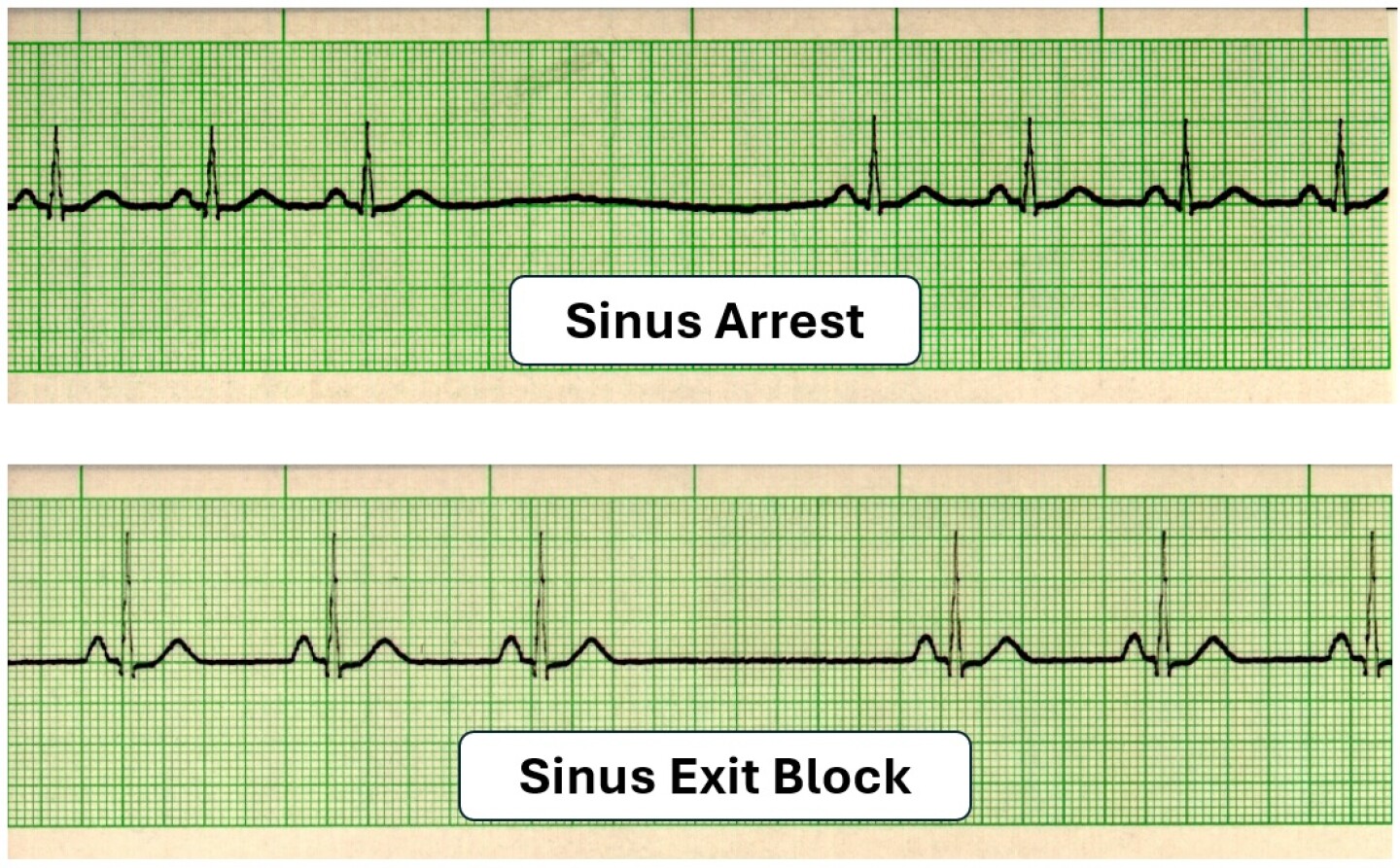
EKG Detective Sinus arrest vs. sinus exit block
During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial to the. Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. There are four primary alterations in the. The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and.
ECG Interpretation in Cardiac Arrest ECG Cases Emergency Medicine Cases
There are four primary alterations in the. Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial to the. The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of.
Case 302020 A 54YearOld Man with Sudden Cardiac Arrest NEJM
During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial to the. There are four primary alterations in the. Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and.
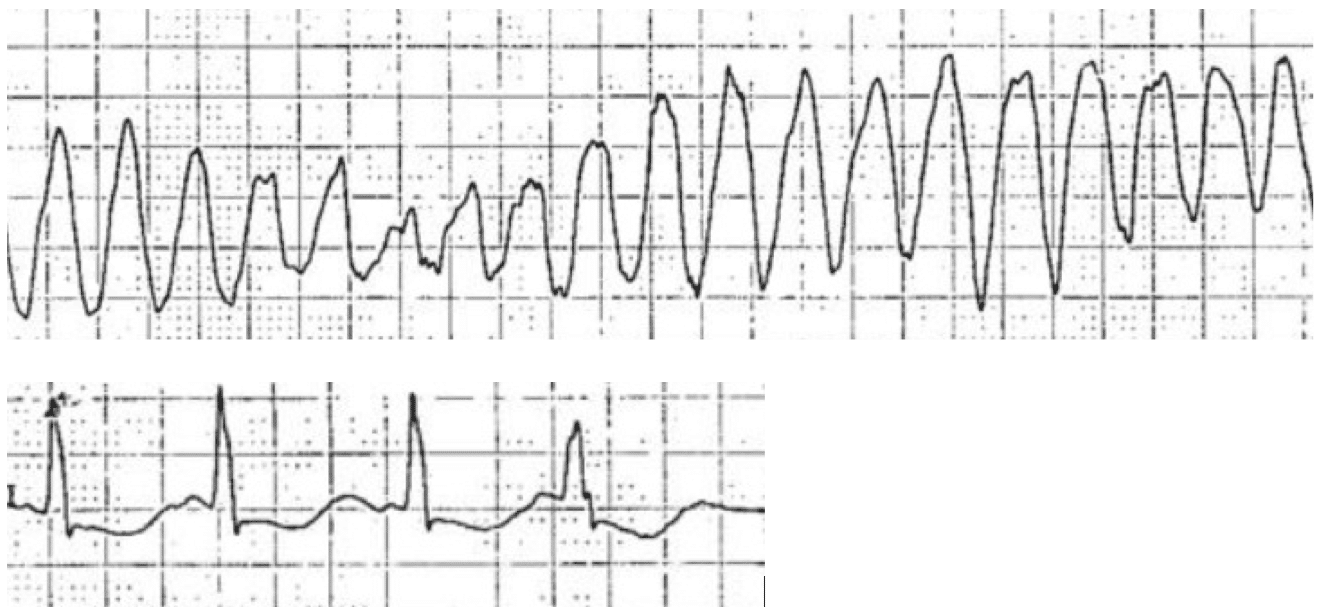
During Cardiac Arrest, Recognition Of Ventricular Fibrillation/Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia (Vf/Vt) As Shockable Rhythms Is Crucial To The.
The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). There are four primary alterations in the. Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart.