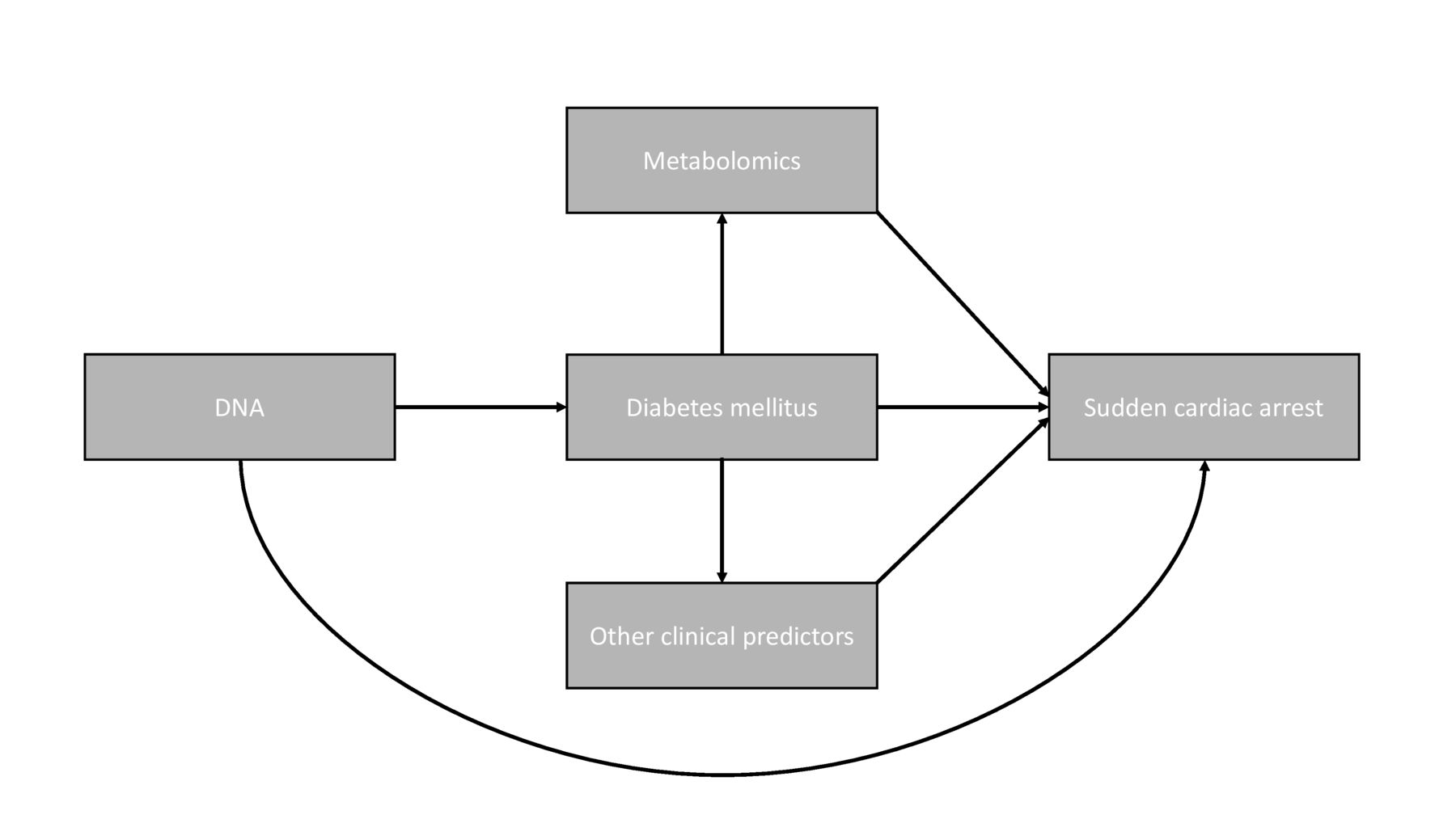
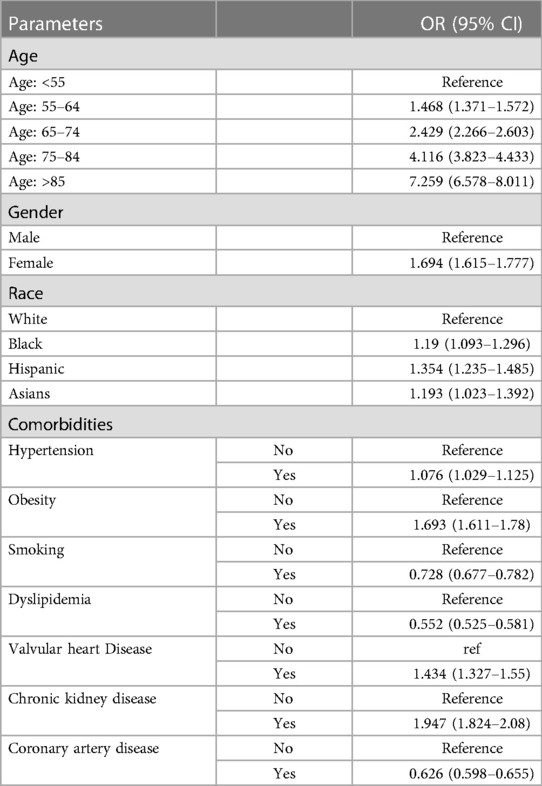
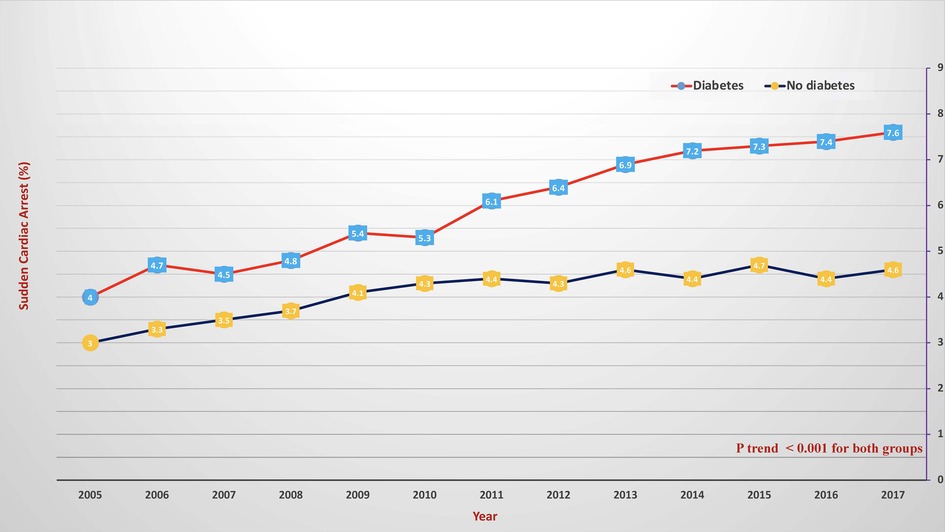
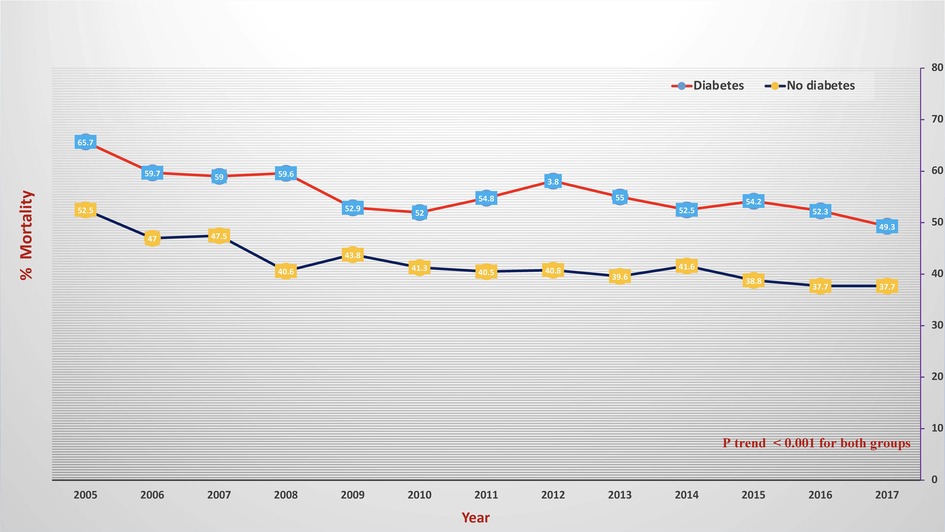
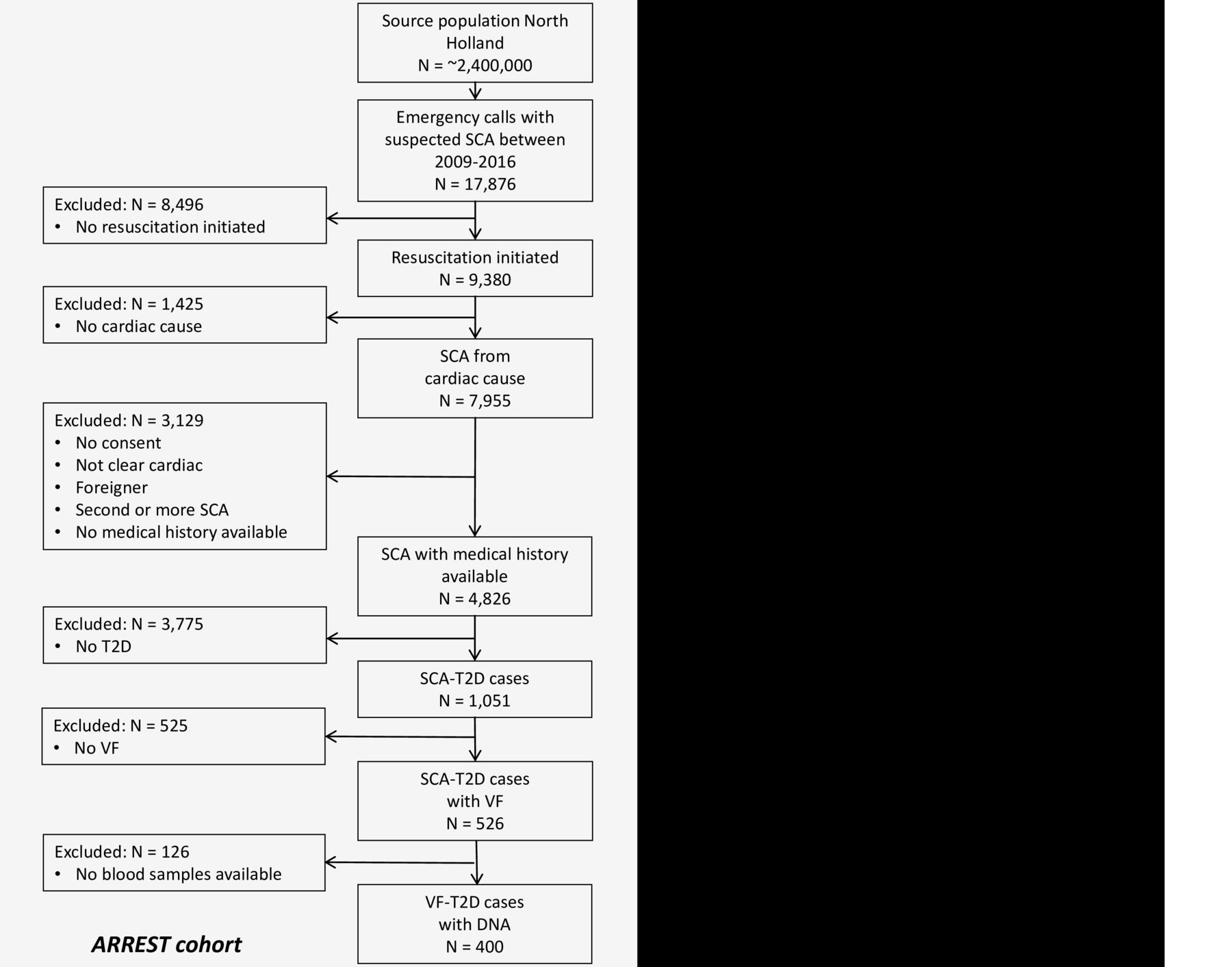
Diabetic Cardiac Arrest - Low fasting glucose and use of certain antibiotics, antipsychotics and prokinetic agents are risk factors for sudden cardiac. Diabetes mellitus (dm) confers an increased risk of sudden cardiac death (scd) independent of its associated cardiovascular.
Diabetes mellitus (dm) confers an increased risk of sudden cardiac death (scd) independent of its associated cardiovascular. Low fasting glucose and use of certain antibiotics, antipsychotics and prokinetic agents are risk factors for sudden cardiac.
Diabetes mellitus (dm) confers an increased risk of sudden cardiac death (scd) independent of its associated cardiovascular. Low fasting glucose and use of certain antibiotics, antipsychotics and prokinetic agents are risk factors for sudden cardiac.
Discovery of predictors of sudden cardiac arrest in diabetes rationale
Diabetes mellitus (dm) confers an increased risk of sudden cardiac death (scd) independent of its associated cardiovascular. Low fasting glucose and use of certain antibiotics, antipsychotics and prokinetic agents are risk factors for sudden cardiac.
Basic Mechanisms of Diabetic Heart Disease Circulation Research
Low fasting glucose and use of certain antibiotics, antipsychotics and prokinetic agents are risk factors for sudden cardiac. Diabetes mellitus (dm) confers an increased risk of sudden cardiac death (scd) independent of its associated cardiovascular.
Frontiers Type 2 diabetes and inhospital sudden cardiac arrest in ST
Low fasting glucose and use of certain antibiotics, antipsychotics and prokinetic agents are risk factors for sudden cardiac. Diabetes mellitus (dm) confers an increased risk of sudden cardiac death (scd) independent of its associated cardiovascular.
Discovery of predictors of sudden cardiac arrest in diabetes rationale
Diabetes mellitus (dm) confers an increased risk of sudden cardiac death (scd) independent of its associated cardiovascular. Low fasting glucose and use of certain antibiotics, antipsychotics and prokinetic agents are risk factors for sudden cardiac.
Is Diabetes Mellitus Associated With Sudden Cardiac Arrest; Cindy’s
Low fasting glucose and use of certain antibiotics, antipsychotics and prokinetic agents are risk factors for sudden cardiac. Diabetes mellitus (dm) confers an increased risk of sudden cardiac death (scd) independent of its associated cardiovascular.
Frontiers Type 2 diabetes and inhospital sudden cardiac arrest in ST
Low fasting glucose and use of certain antibiotics, antipsychotics and prokinetic agents are risk factors for sudden cardiac. Diabetes mellitus (dm) confers an increased risk of sudden cardiac death (scd) independent of its associated cardiovascular.
Frontiers Type 2 diabetes and inhospital sudden cardiac arrest in ST
Diabetes mellitus (dm) confers an increased risk of sudden cardiac death (scd) independent of its associated cardiovascular. Low fasting glucose and use of certain antibiotics, antipsychotics and prokinetic agents are risk factors for sudden cardiac.
Frontiers Type 2 diabetes and inhospital sudden cardiac arrest in ST
Diabetes mellitus (dm) confers an increased risk of sudden cardiac death (scd) independent of its associated cardiovascular. Low fasting glucose and use of certain antibiotics, antipsychotics and prokinetic agents are risk factors for sudden cardiac.
Heart health and diabetes How can diabetic patients tackle cardiac
Diabetes mellitus (dm) confers an increased risk of sudden cardiac death (scd) independent of its associated cardiovascular. Low fasting glucose and use of certain antibiotics, antipsychotics and prokinetic agents are risk factors for sudden cardiac.
Discovery of predictors of sudden cardiac arrest in diabetes rationale
Diabetes mellitus (dm) confers an increased risk of sudden cardiac death (scd) independent of its associated cardiovascular. Low fasting glucose and use of certain antibiotics, antipsychotics and prokinetic agents are risk factors for sudden cardiac.
Low Fasting Glucose And Use Of Certain Antibiotics, Antipsychotics And Prokinetic Agents Are Risk Factors For Sudden Cardiac.
Diabetes mellitus (dm) confers an increased risk of sudden cardiac death (scd) independent of its associated cardiovascular.