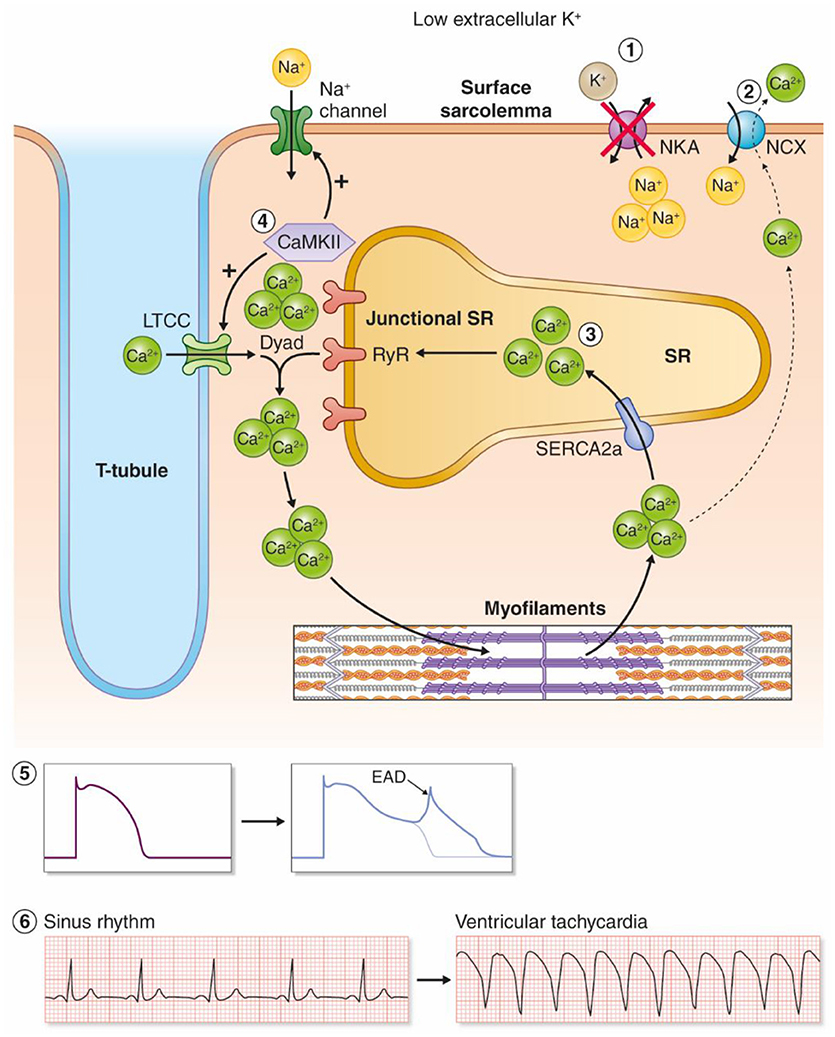
Hypokalemia Cardiac Arrest - Hyperkalemia and hypokalemia are common in admitted patients and recognized as a reversible cause of cardiac arrest. Hypokalemic cardiac arrest is an uncommon occurrence in the emergency department. If cardiac arrest from hypokalemia is imminent (ie, malignant ventricular arrhythmias are present), rapid replacement of potassium is.
If cardiac arrest from hypokalemia is imminent (ie, malignant ventricular arrhythmias are present), rapid replacement of potassium is. Hypokalemic cardiac arrest is an uncommon occurrence in the emergency department. Hyperkalemia and hypokalemia are common in admitted patients and recognized as a reversible cause of cardiac arrest.
If cardiac arrest from hypokalemia is imminent (ie, malignant ventricular arrhythmias are present), rapid replacement of potassium is. Hypokalemic cardiac arrest is an uncommon occurrence in the emergency department. Hyperkalemia and hypokalemia are common in admitted patients and recognized as a reversible cause of cardiac arrest.
Electrophysiology of Hypokalemia and Hyperkalemia Circulation
Hyperkalemia and hypokalemia are common in admitted patients and recognized as a reversible cause of cardiac arrest. If cardiac arrest from hypokalemia is imminent (ie, malignant ventricular arrhythmias are present), rapid replacement of potassium is. Hypokalemic cardiac arrest is an uncommon occurrence in the emergency department.
Hypokalemia Hyperkalemia Ecg
Hyperkalemia and hypokalemia are common in admitted patients and recognized as a reversible cause of cardiac arrest. Hypokalemic cardiac arrest is an uncommon occurrence in the emergency department. If cardiac arrest from hypokalemia is imminent (ie, malignant ventricular arrhythmias are present), rapid replacement of potassium is.
[PDF] A Case of AbirateroneRelated Hypokalemia Leading to Torsades de
If cardiac arrest from hypokalemia is imminent (ie, malignant ventricular arrhythmias are present), rapid replacement of potassium is. Hypokalemic cardiac arrest is an uncommon occurrence in the emergency department. Hyperkalemia and hypokalemia are common in admitted patients and recognized as a reversible cause of cardiac arrest.
[PDF] HypokalemiaInduced Cardiac Arrest Semantic Scholar
If cardiac arrest from hypokalemia is imminent (ie, malignant ventricular arrhythmias are present), rapid replacement of potassium is. Hyperkalemia and hypokalemia are common in admitted patients and recognized as a reversible cause of cardiac arrest. Hypokalemic cardiac arrest is an uncommon occurrence in the emergency department.
Figure 2 from Cardiac Arrest Following Torsades de Pointes Caused by
If cardiac arrest from hypokalemia is imminent (ie, malignant ventricular arrhythmias are present), rapid replacement of potassium is. Hyperkalemia and hypokalemia are common in admitted patients and recognized as a reversible cause of cardiac arrest. Hypokalemic cardiac arrest is an uncommon occurrence in the emergency department.
Dr. Smith's ECG Blog Adding to the many faces of Hypokalemia....
If cardiac arrest from hypokalemia is imminent (ie, malignant ventricular arrhythmias are present), rapid replacement of potassium is. Hypokalemic cardiac arrest is an uncommon occurrence in the emergency department. Hyperkalemia and hypokalemia are common in admitted patients and recognized as a reversible cause of cardiac arrest.
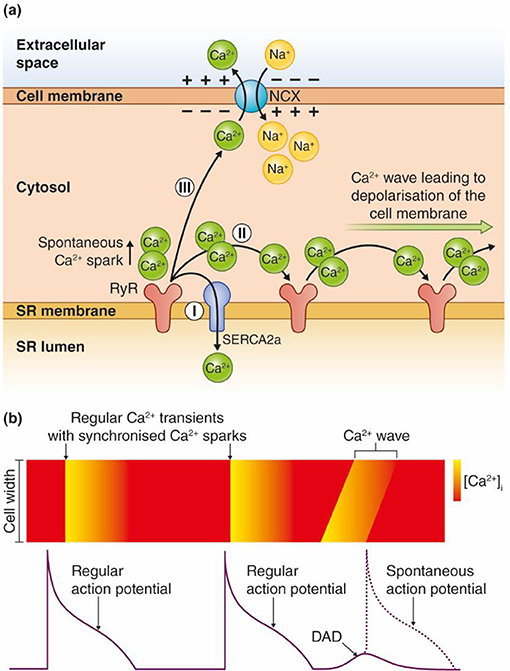
Frontiers HypokalemiaInduced Arrhythmias and Heart Failure New
If cardiac arrest from hypokalemia is imminent (ie, malignant ventricular arrhythmias are present), rapid replacement of potassium is. Hyperkalemia and hypokalemia are common in admitted patients and recognized as a reversible cause of cardiac arrest. Hypokalemic cardiac arrest is an uncommon occurrence in the emergency department.
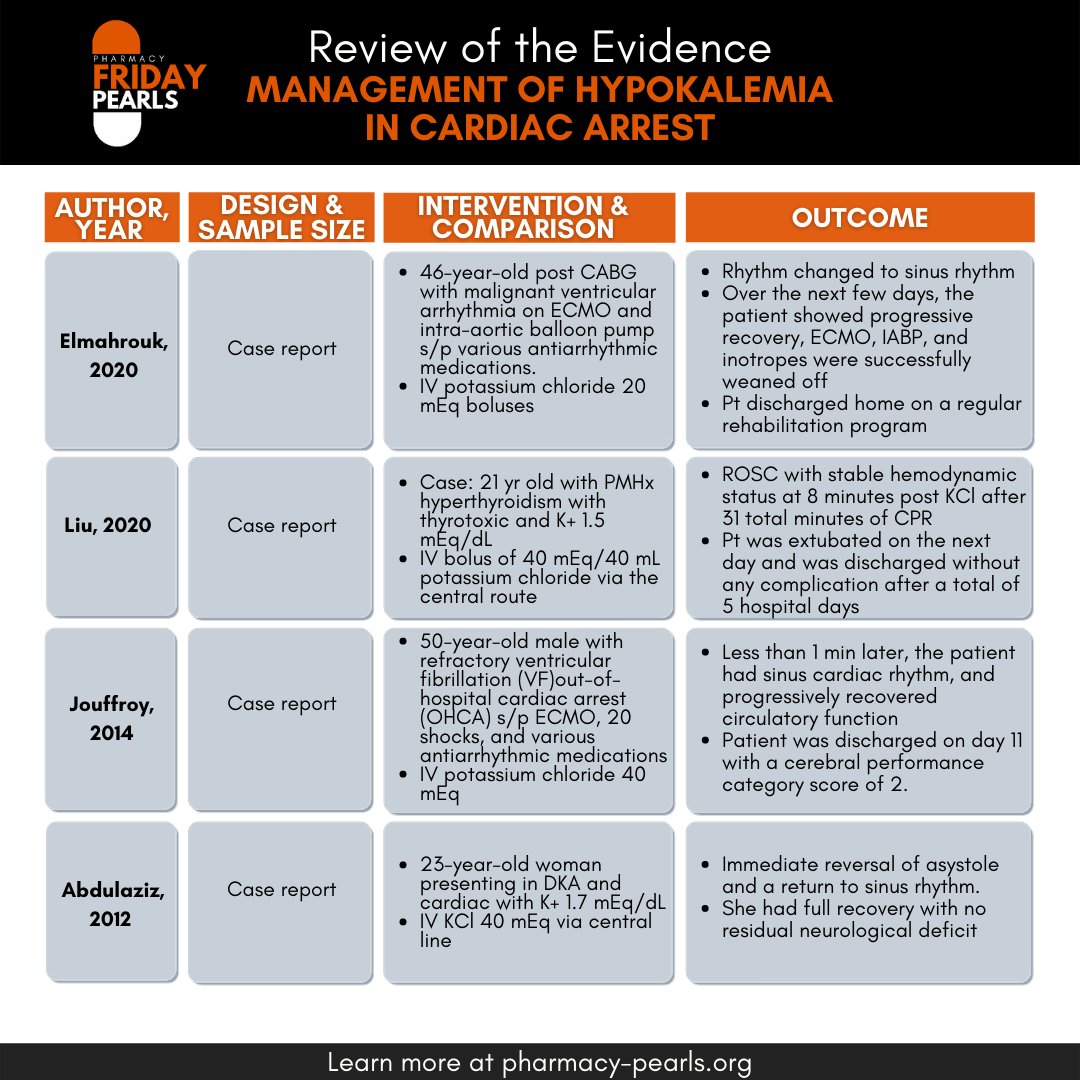
Episode 59. The Management of Hypokalemia in Cardiac Arrest by Jimmy
Hypokalemic cardiac arrest is an uncommon occurrence in the emergency department. Hyperkalemia and hypokalemia are common in admitted patients and recognized as a reversible cause of cardiac arrest. If cardiac arrest from hypokalemia is imminent (ie, malignant ventricular arrhythmias are present), rapid replacement of potassium is.
Zoe Gagnon (ZoeGPharmD) Twitter
If cardiac arrest from hypokalemia is imminent (ie, malignant ventricular arrhythmias are present), rapid replacement of potassium is. Hyperkalemia and hypokalemia are common in admitted patients and recognized as a reversible cause of cardiac arrest. Hypokalemic cardiac arrest is an uncommon occurrence in the emergency department.
Frontiers HypokalemiaInduced Arrhythmias and Heart Failure New
If cardiac arrest from hypokalemia is imminent (ie, malignant ventricular arrhythmias are present), rapid replacement of potassium is. Hyperkalemia and hypokalemia are common in admitted patients and recognized as a reversible cause of cardiac arrest. Hypokalemic cardiac arrest is an uncommon occurrence in the emergency department.
Hypokalemic Cardiac Arrest Is An Uncommon Occurrence In The Emergency Department.
If cardiac arrest from hypokalemia is imminent (ie, malignant ventricular arrhythmias are present), rapid replacement of potassium is. Hyperkalemia and hypokalemia are common in admitted patients and recognized as a reversible cause of cardiac arrest.


![[PDF] A Case of AbirateroneRelated Hypokalemia Leading to Torsades de](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/17a6a2e561f62aa6830ea6ed96d4c79db5248346/2-Figure1-1.png)
![[PDF] HypokalemiaInduced Cardiac Arrest Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/f5355147b2c64959929e8302673d11e28718a45f/3-Figure1-1.png)