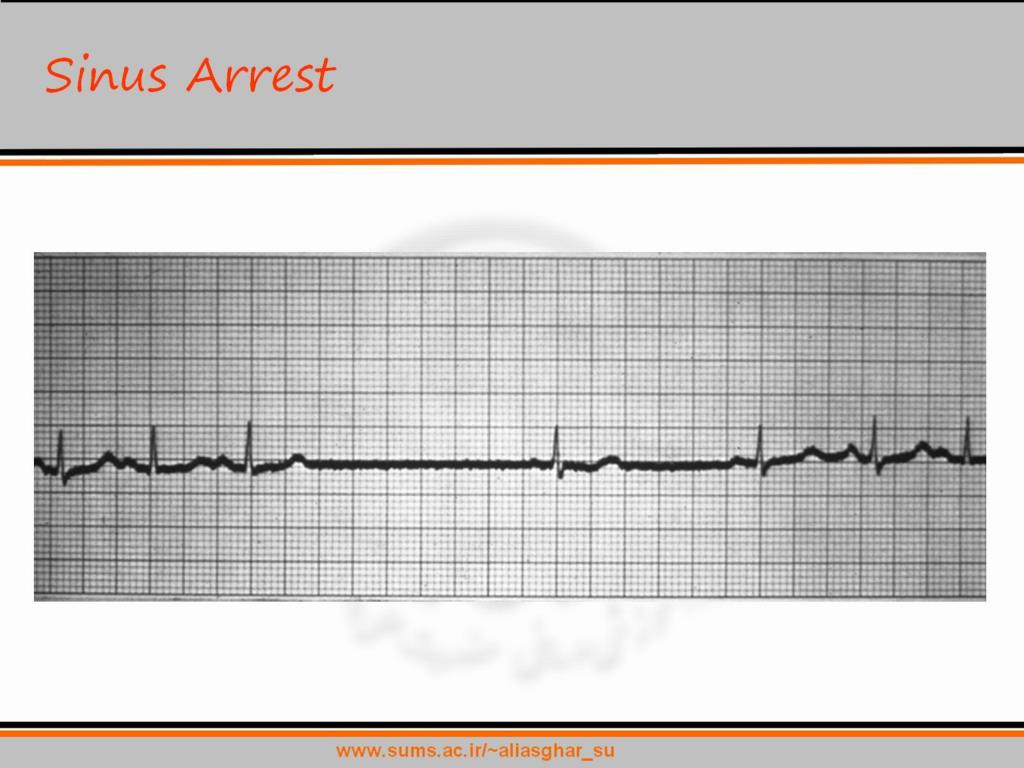
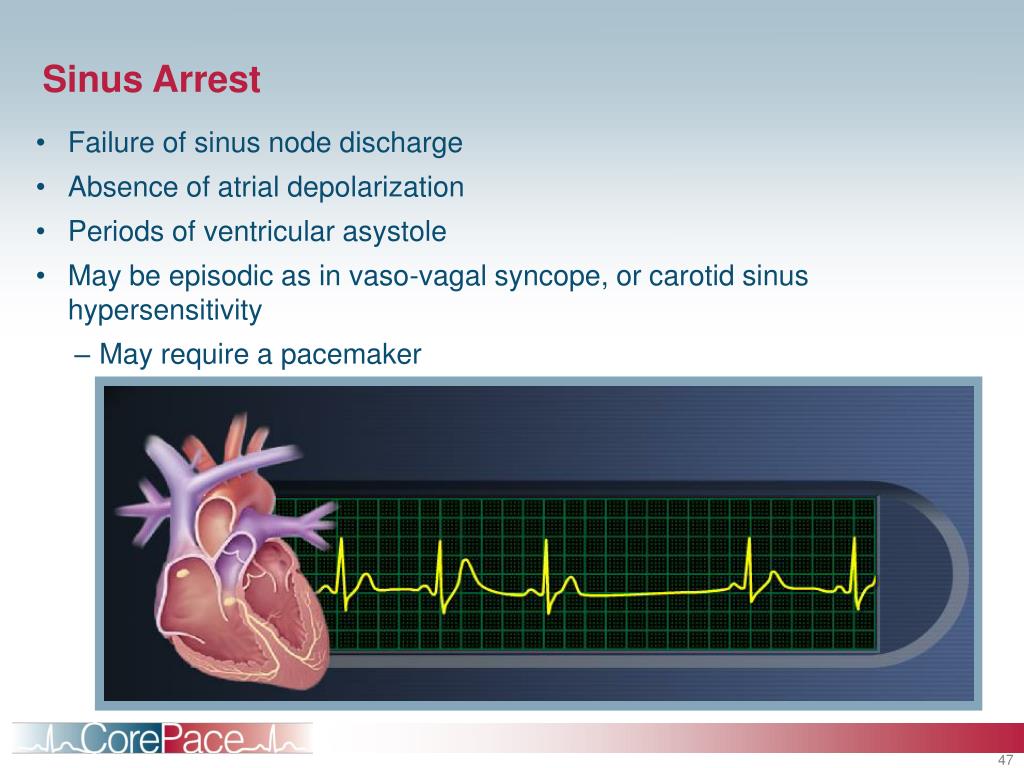
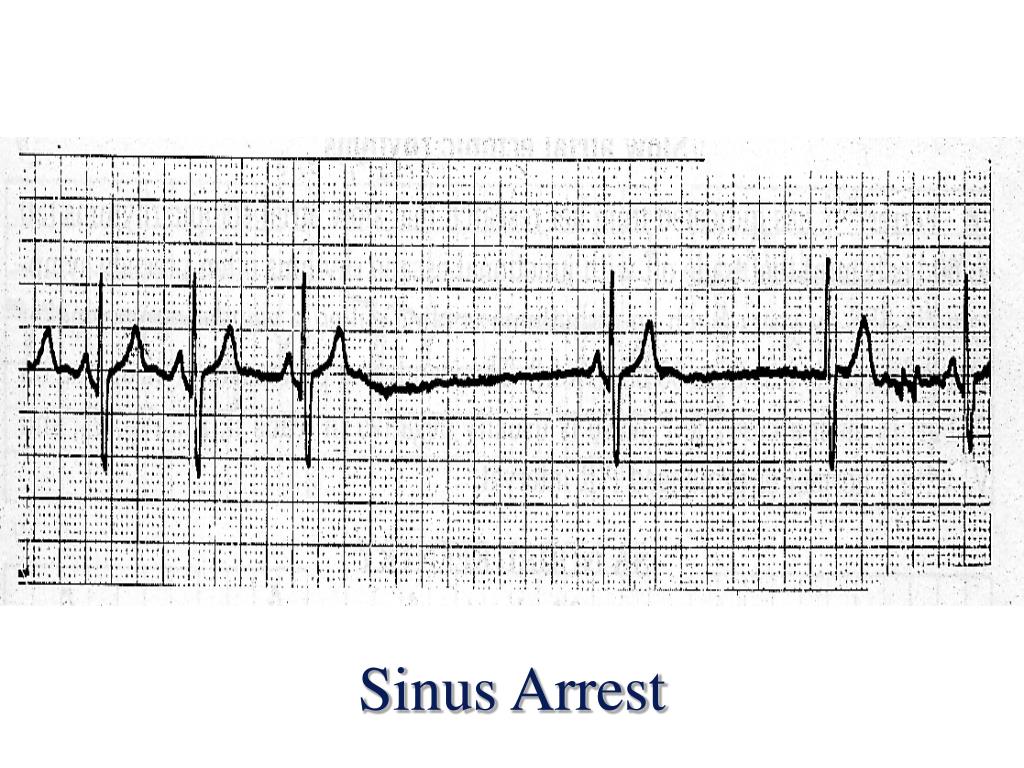
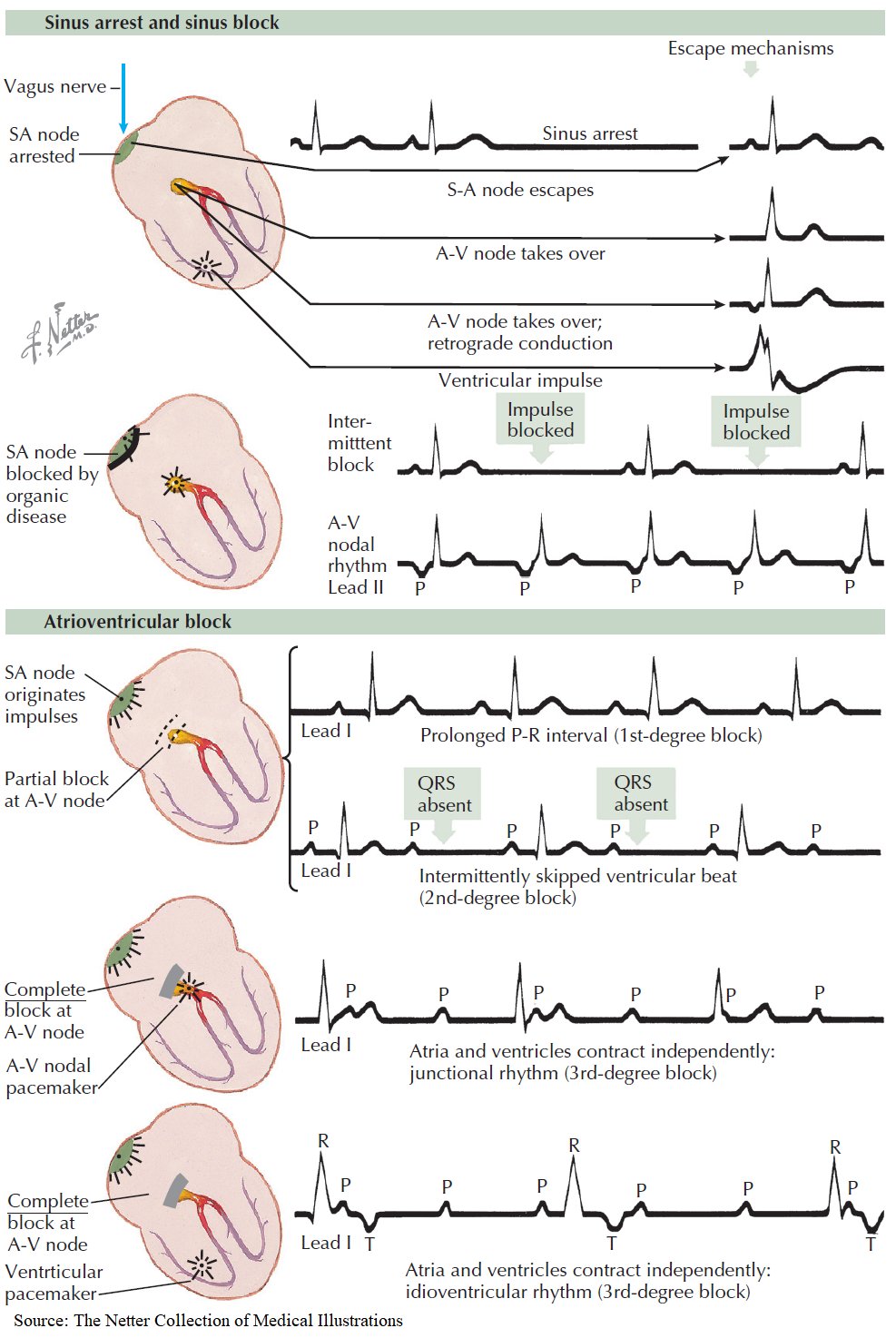
Sinus Arrest Definition - Learn the causes, definitions, ecg diagnosis and clinical management of sinoatrial arrest and sinoatrial pause. Sinus arrest or sinus block is commonly referred to as a pause. It may be due to a problem of generation of the impulse in the sinus node or a. Sinus arrest is a cessation of sinus node activity for a short period. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Sinus arrest implies a failure of atrial activation. Sinoatrial arrest is a medical condition wherein the sinoatrial node of the heart transiently ceases to generate the electrical impulses that. Although sinus arrest commonly is described as a pause in the sinus rhythm. Sinus node dysfunction arises from ischemia and necrosis of pacemaker cells because of a reduction in arterial blood. This occurs when there is a conduction block causing in the sinus node.
It may be due to a problem of generation of the impulse in the sinus node or a. Sinus node dysfunction arises from ischemia and necrosis of pacemaker cells because of a reduction in arterial blood. Sinus arrest implies a failure of atrial activation. Sinoatrial arrest is a medical condition wherein the sinoatrial node of the heart transiently ceases to generate the electrical impulses that. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. This occurs when there is a conduction block causing in the sinus node. Although sinus arrest commonly is described as a pause in the sinus rhythm. Learn the causes, definitions, ecg diagnosis and clinical management of sinoatrial arrest and sinoatrial pause. Sinus arrest or sinus block is commonly referred to as a pause. Sinus arrest is a cessation of sinus node activity for a short period.
Sinus arrest implies a failure of atrial activation. It may be due to a problem of generation of the impulse in the sinus node or a. Although sinus arrest commonly is described as a pause in the sinus rhythm. Sinus arrest is a cessation of sinus node activity for a short period. Sinoatrial arrest is a medical condition wherein the sinoatrial node of the heart transiently ceases to generate the electrical impulses that. This occurs when there is a conduction block causing in the sinus node. Learn the causes, definitions, ecg diagnosis and clinical management of sinoatrial arrest and sinoatrial pause. Sinus arrest or sinus block is commonly referred to as a pause. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Sinus node dysfunction arises from ischemia and necrosis of pacemaker cells because of a reduction in arterial blood.
PPT Rhythm Analysis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6971486
Sinoatrial arrest is a medical condition wherein the sinoatrial node of the heart transiently ceases to generate the electrical impulses that. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Sinus arrest implies a failure of atrial activation. Sinus node dysfunction arises from ischemia and necrosis of pacemaker cells because.
ECG Educator Blog Sinus Arrest
Sinus arrest or sinus block is commonly referred to as a pause. This occurs when there is a conduction block causing in the sinus node. Sinoatrial arrest is a medical condition wherein the sinoatrial node of the heart transiently ceases to generate the electrical impulses that. Learn the causes, definitions, ecg diagnosis and clinical management of sinoatrial arrest and sinoatrial.
Sinus Rhythms BMH/Tele
Sinoatrial arrest is a medical condition wherein the sinoatrial node of the heart transiently ceases to generate the electrical impulses that. Sinus arrest is a cessation of sinus node activity for a short period. Sinus arrest or sinus block is commonly referred to as a pause. Sinus node dysfunction arises from ischemia and necrosis of pacemaker cells because of a.
PPT Arrhythmias and Devices Module 1 PowerPoint Presentation, free
It may be due to a problem of generation of the impulse in the sinus node or a. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Sinus arrest implies a failure of atrial activation. Although sinus arrest commonly is described as a pause in the sinus rhythm. Sinus arrest.
Electrocardiogram Show Sinus Arrest Pattern. Stock Vector
Although sinus arrest commonly is described as a pause in the sinus rhythm. Sinoatrial arrest is a medical condition wherein the sinoatrial node of the heart transiently ceases to generate the electrical impulses that. Sinus node dysfunction arises from ischemia and necrosis of pacemaker cells because of a reduction in arterial blood. Sinus arrest implies a failure of atrial activation..
ECG Educator Blog Sinus Arrest
Sinus arrest implies a failure of atrial activation. Although sinus arrest commonly is described as a pause in the sinus rhythm. It may be due to a problem of generation of the impulse in the sinus node or a. Learn the causes, definitions, ecg diagnosis and clinical management of sinoatrial arrest and sinoatrial pause. Sinoatrial arrest is a medical condition.
Sinus Arrest or Sinus Pause YouTube
Sinus arrest implies a failure of atrial activation. This occurs when there is a conduction block causing in the sinus node. Although sinus arrest commonly is described as a pause in the sinus rhythm. Sinoatrial arrest is a medical condition wherein the sinoatrial node of the heart transiently ceases to generate the electrical impulses that. Sinus arrest or sinus block.
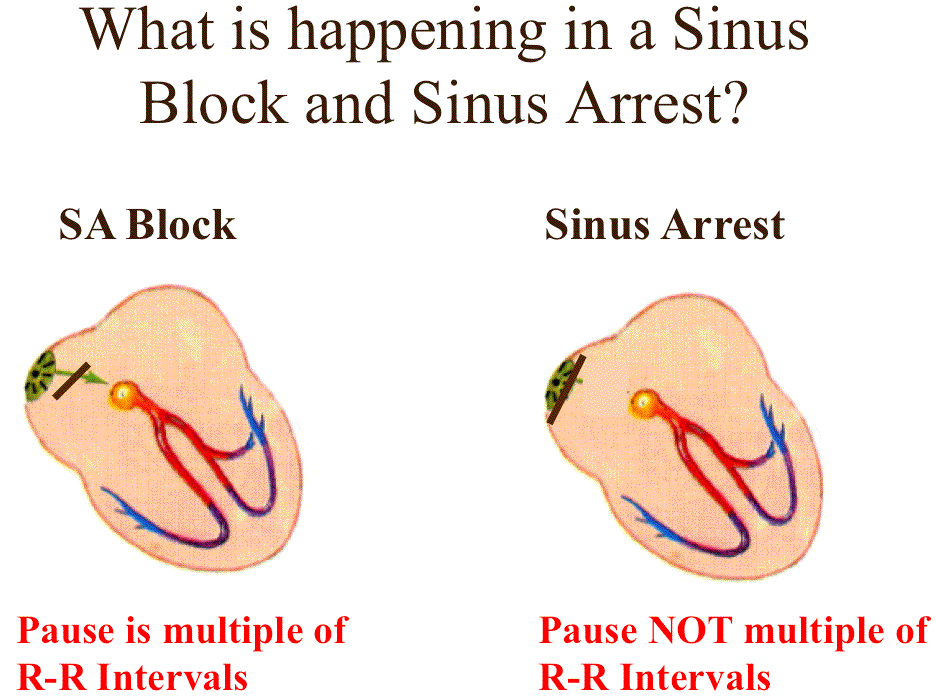
SA Block and Sinus Arrest
Sinus arrest or sinus block is commonly referred to as a pause. It may be due to a problem of generation of the impulse in the sinus node or a. Sinoatrial arrest is a medical condition wherein the sinoatrial node of the heart transiently ceases to generate the electrical impulses that. Although sinus arrest commonly is described as a pause.
PPT Cardiac Dysrhythmias PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Sinus arrest implies a failure of atrial activation. Sinus arrest is a cessation of sinus node activity for a short period. It may be due to a problem of generation of the impulse in the sinus node or a. Sinus arrest or sinus block is commonly referred to as a pause. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or.
Manual Of Medicine on Twitter "Sinus Arrest, Sinus Block and
Sinus arrest is a cessation of sinus node activity for a short period. Sinus arrest implies a failure of atrial activation. Although sinus arrest commonly is described as a pause in the sinus rhythm. Sinus arrest or sinus block is commonly referred to as a pause. Sinoatrial arrest is a medical condition wherein the sinoatrial node of the heart transiently.
It May Be Due To A Problem Of Generation Of The Impulse In The Sinus Node Or A.
Sinoatrial arrest is a medical condition wherein the sinoatrial node of the heart transiently ceases to generate the electrical impulses that. This occurs when there is a conduction block causing in the sinus node. Sinus arrest is a cessation of sinus node activity for a short period. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;.
Sinus Arrest Implies A Failure Of Atrial Activation.
Learn the causes, definitions, ecg diagnosis and clinical management of sinoatrial arrest and sinoatrial pause. Sinus arrest or sinus block is commonly referred to as a pause. Although sinus arrest commonly is described as a pause in the sinus rhythm. Sinus node dysfunction arises from ischemia and necrosis of pacemaker cells because of a reduction in arterial blood.