T Causes Of Reversible Cardiac Arrest - Treat each traumatic injury as needed to correct any reversible cause or contributing factor to the pulseless arrest. The 5 h's and 5 t's that may cause cardiac arrest 5 h's 5 t's hypovolemia tension pneumothorax hypoxia tamponade (cardiac) hydrogen ion. During any cardiac arrest, part of the resuscitation effort must focus on identifying and treating potentially reversible causes — the conditions.
Treat each traumatic injury as needed to correct any reversible cause or contributing factor to the pulseless arrest. The 5 h's and 5 t's that may cause cardiac arrest 5 h's 5 t's hypovolemia tension pneumothorax hypoxia tamponade (cardiac) hydrogen ion. During any cardiac arrest, part of the resuscitation effort must focus on identifying and treating potentially reversible causes — the conditions.
The 5 h's and 5 t's that may cause cardiac arrest 5 h's 5 t's hypovolemia tension pneumothorax hypoxia tamponade (cardiac) hydrogen ion. During any cardiac arrest, part of the resuscitation effort must focus on identifying and treating potentially reversible causes — the conditions. Treat each traumatic injury as needed to correct any reversible cause or contributing factor to the pulseless arrest.
Many cardiac arrest conditions are reversible, determining and treating
During any cardiac arrest, part of the resuscitation effort must focus on identifying and treating potentially reversible causes — the conditions. The 5 h's and 5 t's that may cause cardiac arrest 5 h's 5 t's hypovolemia tension pneumothorax hypoxia tamponade (cardiac) hydrogen ion. Treat each traumatic injury as needed to correct any reversible cause or contributing factor to the.
Hs and Ts 8 Reversible Causes of Cardiac Arrest Heart Start CPR
Treat each traumatic injury as needed to correct any reversible cause or contributing factor to the pulseless arrest. The 5 h's and 5 t's that may cause cardiac arrest 5 h's 5 t's hypovolemia tension pneumothorax hypoxia tamponade (cardiac) hydrogen ion. During any cardiac arrest, part of the resuscitation effort must focus on identifying and treating potentially reversible causes —.
Reversible Causes of Cardiac Arrest Hs and Ts Mnemonic H's & T's
The 5 h's and 5 t's that may cause cardiac arrest 5 h's 5 t's hypovolemia tension pneumothorax hypoxia tamponade (cardiac) hydrogen ion. During any cardiac arrest, part of the resuscitation effort must focus on identifying and treating potentially reversible causes — the conditions. Treat each traumatic injury as needed to correct any reversible cause or contributing factor to the.
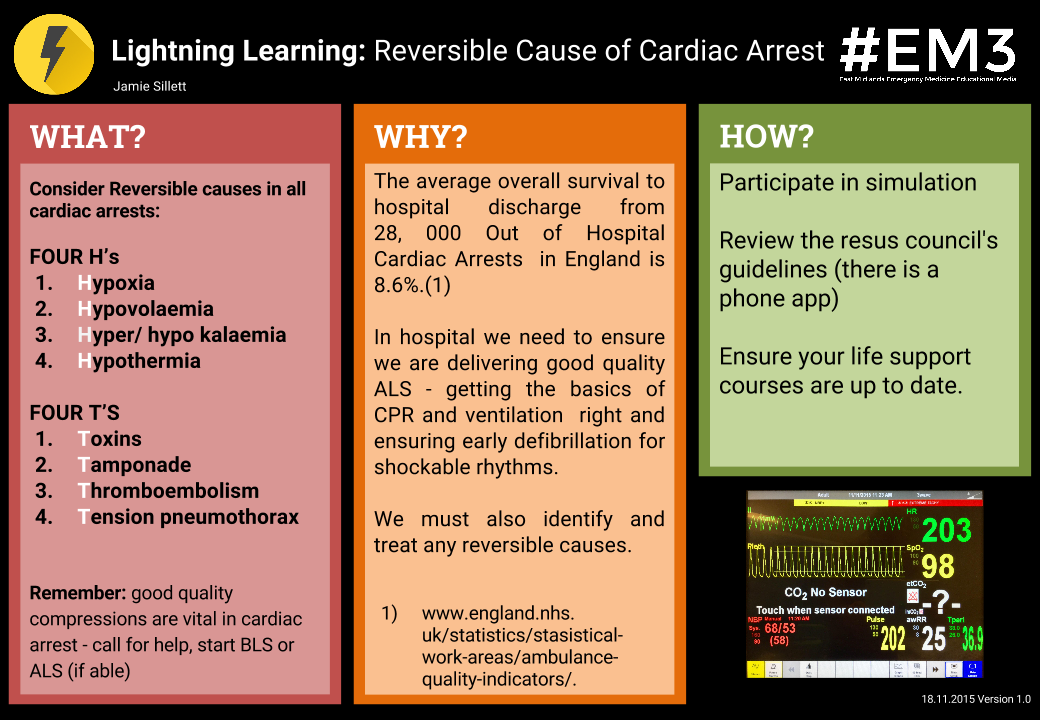
Lightning Learning Cardiac Arrest H's & T's — EM3
Treat each traumatic injury as needed to correct any reversible cause or contributing factor to the pulseless arrest. During any cardiac arrest, part of the resuscitation effort must focus on identifying and treating potentially reversible causes — the conditions. The 5 h's and 5 t's that may cause cardiac arrest 5 h's 5 t's hypovolemia tension pneumothorax hypoxia tamponade (cardiac).
Hs and Ts 8 Reversible Causes of Cardiac Arrest Heart Start CPR
Treat each traumatic injury as needed to correct any reversible cause or contributing factor to the pulseless arrest. The 5 h's and 5 t's that may cause cardiac arrest 5 h's 5 t's hypovolemia tension pneumothorax hypoxia tamponade (cardiac) hydrogen ion. During any cardiac arrest, part of the resuscitation effort must focus on identifying and treating potentially reversible causes —.
Something you will hear when learning ACLS is to CHECK YOUR Hs & Ts
During any cardiac arrest, part of the resuscitation effort must focus on identifying and treating potentially reversible causes — the conditions. The 5 h's and 5 t's that may cause cardiac arrest 5 h's 5 t's hypovolemia tension pneumothorax hypoxia tamponade (cardiac) hydrogen ion. Treat each traumatic injury as needed to correct any reversible cause or contributing factor to the.
Many cardiac arrest conditions are reversible, determining and treating
The 5 h's and 5 t's that may cause cardiac arrest 5 h's 5 t's hypovolemia tension pneumothorax hypoxia tamponade (cardiac) hydrogen ion. During any cardiac arrest, part of the resuscitation effort must focus on identifying and treating potentially reversible causes — the conditions. Treat each traumatic injury as needed to correct any reversible cause or contributing factor to the.
Understanding Hs and Ts in Cardiac Arrest 💖 Caring For Care
Treat each traumatic injury as needed to correct any reversible cause or contributing factor to the pulseless arrest. The 5 h's and 5 t's that may cause cardiac arrest 5 h's 5 t's hypovolemia tension pneumothorax hypoxia tamponade (cardiac) hydrogen ion. During any cardiac arrest, part of the resuscitation effort must focus on identifying and treating potentially reversible causes —.
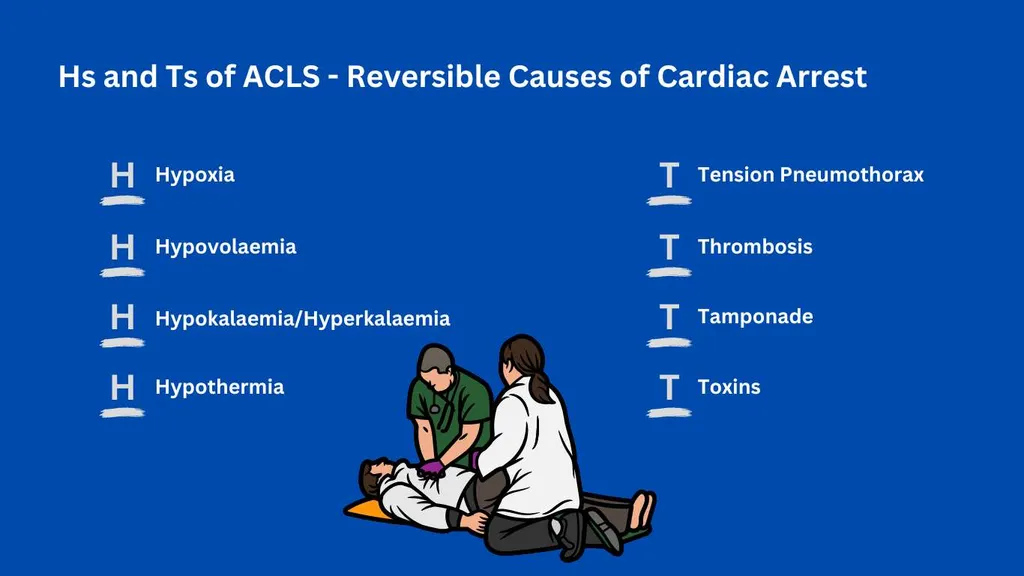
Reversible Causes of Cardiac Arrest The Four Hs and Four Ts
The 5 h's and 5 t's that may cause cardiac arrest 5 h's 5 t's hypovolemia tension pneumothorax hypoxia tamponade (cardiac) hydrogen ion. Treat each traumatic injury as needed to correct any reversible cause or contributing factor to the pulseless arrest. During any cardiac arrest, part of the resuscitation effort must focus on identifying and treating potentially reversible causes —.
Reversible Causes of Cardiac Arrest The Four Hs and Four Ts
The 5 h's and 5 t's that may cause cardiac arrest 5 h's 5 t's hypovolemia tension pneumothorax hypoxia tamponade (cardiac) hydrogen ion. Treat each traumatic injury as needed to correct any reversible cause or contributing factor to the pulseless arrest. During any cardiac arrest, part of the resuscitation effort must focus on identifying and treating potentially reversible causes —.
Treat Each Traumatic Injury As Needed To Correct Any Reversible Cause Or Contributing Factor To The Pulseless Arrest.
During any cardiac arrest, part of the resuscitation effort must focus on identifying and treating potentially reversible causes — the conditions. The 5 h's and 5 t's that may cause cardiac arrest 5 h's 5 t's hypovolemia tension pneumothorax hypoxia tamponade (cardiac) hydrogen ion.



.png)